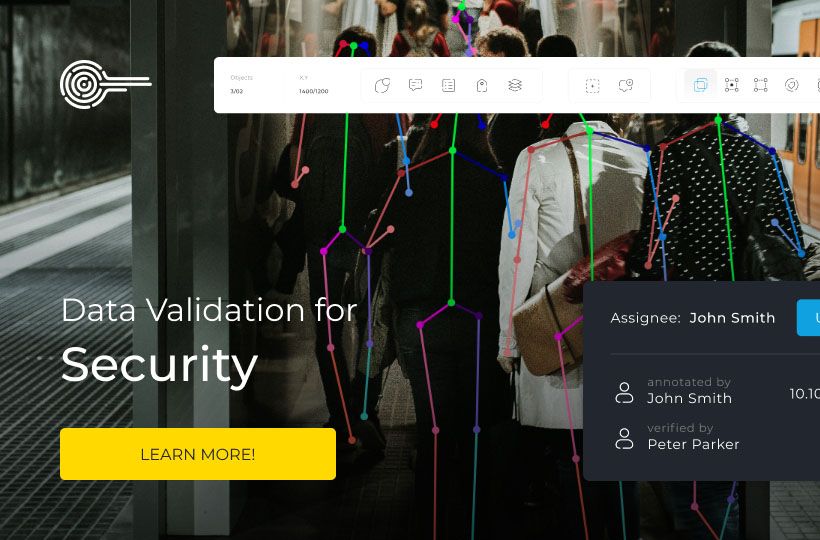
Data Annotation Compliance: GDPR compliance, HIPAA regulations, and Data Privacy Laws
AI development requires careful handling of personal data to ensure regulatory compliance and data protection. Regulations like GDPR compliance, HIPAA regulations, and other data privacy laws require strict protocols for labeling processes, consent management, and breach prevention.
Even unintentional mistakes during AI training can violate privacy rights.
To reconcile innovation with legal obligations, specialized expertise in secure data labeling practices is required that aligns technical workflows with regulatory expectations. Privacy must be prioritized at every step.
Quick Take
- GDPR and HIPAA set the rules for handling sensitive information in AI projects, especially regarding annotation security, data governance, and privacy-by-design principles.
- Consent management and accurate labeling prevent regulatory violations.
- Fines for non-compliance exceed seven figures for businesses.
- Specialized protocols combine innovation with legal requirements.

Overview of GDPR and Data Annotation Standards
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) outlines the fundamental principles for the collection, storage, processing, and use of data of European Union citizens, forming the foundation of EU regulations on data protection and annotation security. It aims to ensure transparency in the handling of personal information and to give users control over how their data is used. In the field of data annotation, the markup process involves working with sensitive information that contains identifiable data.
The GDPR requires that all data used to train artificial intelligence models be depersonalized or anonymized so that it is not possible to identify a specific individual. Annotation companies must ensure data minimization, restrict access to source material, and implement technical and organizational security measures. Each processing step must be documented, and contractors and annotators must adhere to the same standards.
In addition to the GDPR, there are quality and ethical standards for data annotation. These include ISO/IEC 27001 for information security management, ISO/IEC 25012, which describes data quality, and industry guidelines for transparency and reproducibility of annotations. A properly organized annotation process involves accuracy, consistency between performers, metadata capture, and quality control. This enhances the reliability of AI models and facilitates compliance with legal requirements.

GDPR compliance of data annotations in AI projects
GDPR compliance starts with risk reduction. Personal data required for training the model is processed under strict data governance and privacy-by-design principles. The data should be anonymized or pseudonymized so that the individual cannot be identified without additional information.
Purpose limitation. Data collected and prepared for a specific AI project is used only within the agreed-upon purposes. Using annotations for purposes other than those for which consent was given carries a risk of infringement.
Transparency and rights of subjects. Individuals whose data are used must be informed that their data may be annotated, the purpose of the annotation, who the operator is, and their rights.
Security and risk management. Data annotation involves working with large amounts of information, which can sometimes be sensitive and confidential. Therefore, access should be granted only to authorized persons. Data transfer and storage should be protected, and a policy should be in place for logging, monitoring, and deleting or archiving data once its purposes have been fulfilled.
Documentation and auditing. Each stage of the work should be documented. Annotation contractors must adhere to the same standards as the leading operator.
Retention no longer than necessary. After the project is completed, the data must be returned or securely deleted.
Keylabs Security
The workflow on the Keylabs platform is built with the requirements of GDPR compliance and the international information security standard ISO 27001 in mind, ensuring full annotation security and regulatory compliance. It supports data management and workflows in a way that ensures data integrity and guarantees the final annotated data is accurate, consistent, and ready for use in AI and machine learning projects.
This means that annotation, verification, access control, and reporting are integrated into the solution, which helps maintain security from a technical perspective.
Therefore, the Keylabs platform is a secure option for AI projects that utilize personal or sensitive data. Our tools are GDPR and ISO 27001 compliant, which simplifies internal risk assessment and compliance with legal requirements.
Data Privacy and Security in Data Annotation
When data annotation is performed, organizations must ensure that privacy and security are maintained. A balance between these aspects is critical to comply with legislation such as GDPR and maintain user trust. Excessive anonymization reduces the value of data for training AI models, while excessive openness creates risks of leakage. The optimal solution is a combination of technical, organizational, and policy measures that allow data to be handled without compromising its quality or security.
Implementing Secure Data Labeling Practices
AI teams support speed and security by combining human expertise with advanced technology.
Human-guided labeling accurately interprets complex scenarios while maintaining annotation security and data protection. Subject matter experts perform healthcare data analysis and legal document review with context awareness. Tight access controls ensure that only authorized teams view sensitive materials while performing these tasks.
Automated tools accelerate large-scale projects, such as labeling satellite imagery. Pre-labeling with AI, featuring built-in security measures that mask personal identifiers before processing, significantly speeds up the workflow.
A hybrid approach that combines annotator validation with automated annotation of repetitive scenarios reduces workload while maintaining privacy standards.
This approach creates a feedback loop that improves both accuracy and security. Quality checks include:
- Real-time monitoring of labeling activities.
- Encrypted storage logs for raw materials and processed materials.
- Dynamic access permissions based on project requirements.
Military-grade encryption during file transfers and pseudonymization methods for sensitive projects, continuous vulnerability scanning, and multi-factor authentication build trust with both customers and regulators.
Navigating Global Data Protection Rules for AI Training Data
Global AI initiatives face a range of data privacy laws and EU regulations that vary by region, making consistent regulatory compliance essential. Address these complexities with adaptive frameworks that cater to local requirements and sustain project momentum.
Comparing Core Framework Requirements
Three rules shape the current development of AI:
Implement unified systems that account for overlapping regulations and ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. For example, medical AI projects serving transatlantic patients combine:
- HiPAA-compliant, encrypted, and annotated data.
- GDPR-compliant user dashboards.
- CCPA-compliant automated data deletion workflows.
This approach reduces legal risks compared to fragmented solutions. As a result, customers benefit from strategies that combine GDPR compliance, HIPAA regulations, and global data governance principles for stronger data protection and regulatory compliance.
Data Leakage Prevention and Raw Data Management Strategies
In data preparation and annotation processes, one of the main challenges is to prevent information leakage and properly manage raw data. Such data contains confidential or personal information, so it must be handled with care.
FAQ
How do regulations like GDPR impact AI training workflows?
These regulations impact AI training workflows by requiring transparency, data minimization, and privacy protections at all stages of processing.
What methods prevent sensitive information from being exposed during labeling?
Anonymization, pseudonymization, access control, data encryption, and the use of secure environments for AI operations.
Why combine manual and automated approaches for compliance?
Combining manual and automated approaches provides accuracy in verification, flexibility in decision-making, and consistency in compliance across all stages of data processing.
How do global regulations differ for AI initiatives in healthcare and for consumers?
Global health regulations prioritize patient safety, the ethical use of medical data, and clinical validation, whereas consumer regulations emphasize privacy protection, algorithm transparency, and non-discrimination.
What steps can be taken to reduce data breaches in collaborative annotation environments?
Data breaches can be reduced by restricting access by role, encrypting data, monitoring user actions, anonymizing information, and conducting regular security audits.