Surgical AI Developers Need the Right Tools
Robots can help surgeons to perform some of the most complex medical procedures. Surgeons use these devices to perform extremely precise micro-surgeries. The precision movement of robots helps surgeons maintain control of complex procedures and helps to avoid post-surgical infections.
Now AI developers are looking for ways in which machine learning can further help surgeons and improve outcomes for patients. Computer vision based AI models can support surgeons, guide treatment and even perform surgeries autonomously.

However, in order for these exciting applications to reach their potential AI companies need access to high quality annotated training data. Finding the right image and video annotation tool is an important part of this process. Keylabs is an annotation platform that supports innovation in medical AI.
Firstly, this blog will look at AI systems that help train and guide surgeons. Secondly, we will look at how AI can prepare patients for surgery. And finally, we will look to the future of fully automated AI surgery.
Helping surgeons
One promising application for AI in surgery is monitoring surgical procedures and providing feedback for surgeons. Computer vision systems can be trained to track the movements of surgeons hands and surgical implements. Using this data, algorithms and medical professionals can assess the skill of surgeons.
As a result of this research and development surgeons have a powerful new training tool which can increase performance across the sector. AI systems can also be taught to recognise the distinct phases of any operation. Annotated video data allows machine learning algorithms to track the progress of an operation and offer help and advice at the right time.
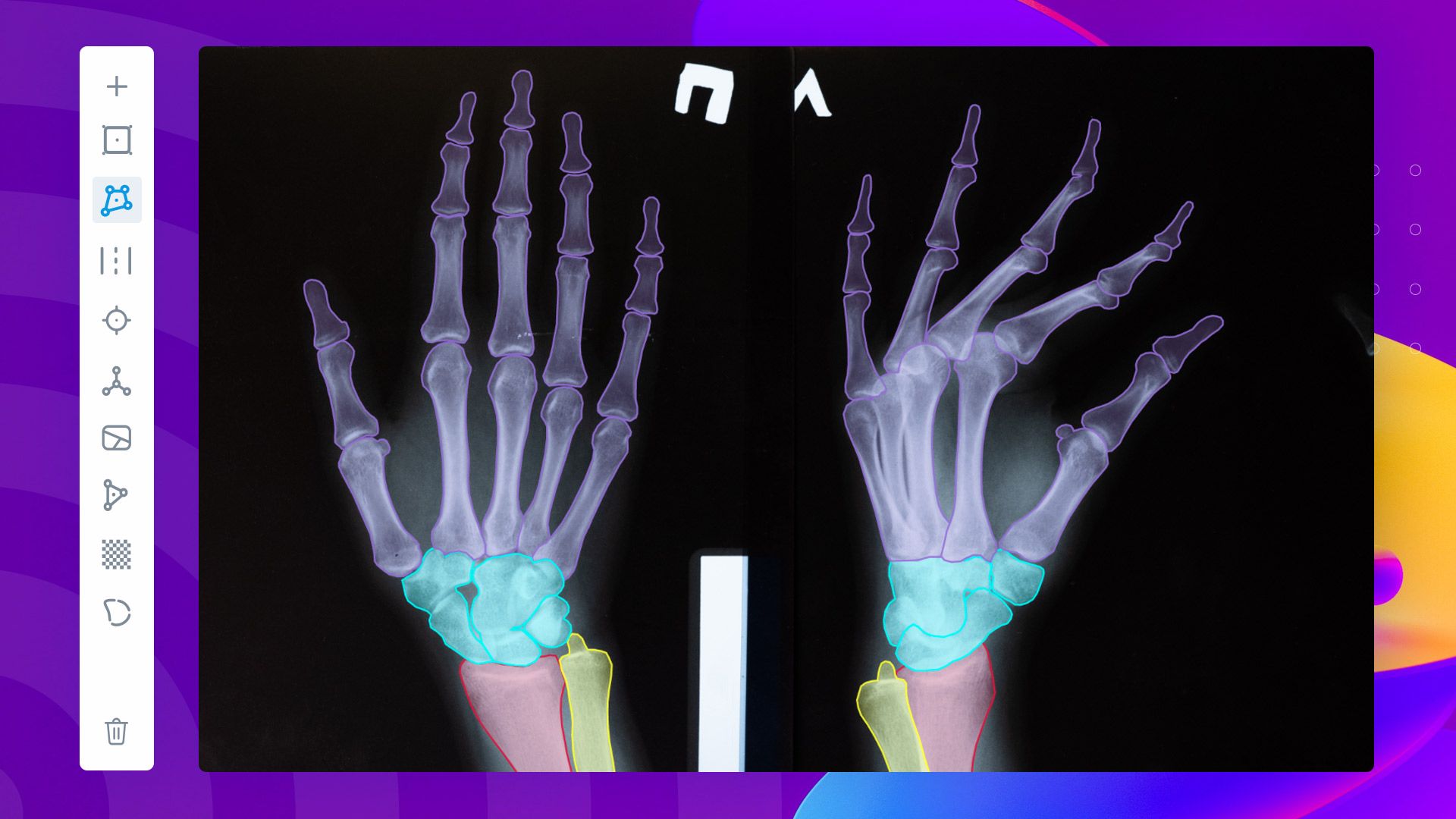
Preparing patients
Planning a surgical procedure can sometimes be an inexact science. Each patient is different and each surgery can be affected by thousands of different variables. Spinal surgery is done by bending small rods into shape and then attaching them to injured or deformed vertebrae.
This surgery is currently heavily reliant on the judgement of the surgeon performing it. This can lead to wide ranging outcomes for patients. AI models can reduce this variability by giving surgeons a more detailed view of a patient's spines before surgery. If surgeons know more about the alignment of a patient's spine they can craft spine rods that will work more effectively.
The complete package
In the future it may be possible for robots to carry out operations entirely by themselves. Computer vision AI could lead to machines doing simple procedures on a regular basis, freeing up human surgeons for more complex and sensitive tasks. Robots have already performed surgery successfully on animal subjects, and it may only be a matter of time before human trials are underway.
AI is most useful for repetitive actions, such as suturing and valve repair. This capability could allow robots to support surgeons, for example stitching up wounds at the end of an operation. However, in order to develop further this technology needs to learn quickly. As more AI systems are developed they will be able to learn from one another. This connected pool of surgical data will lead to better performing models.
Keylabs data annotation tools
Surgical AI could transform patient care and make surgery faster and safer. However, AI developers need annotated training data to guarantee this. Keylabs is a platform developed by annotation experts with the aim of accelerating the annotation process. The tool has a proven track record of handling large datasets without performance being affected.
In addition Keylabs features powerful project management options. For example a work sharing system that links annotators and verifiers and distributes tasks between them efficiently. Streamline your annotation project with Keylabs.