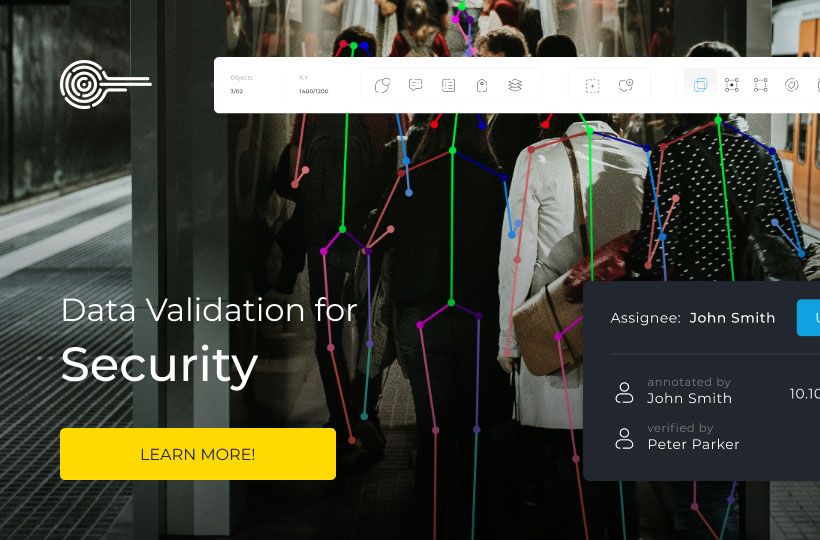
Data Privacy Rules in Annotation Projects
When handling personal data during the labeling process, unique risks arise. Traditional methods rely on direct human interaction, which creates vulnerabilities. Even minor oversights can lead to costly incidents, particularly in industries such as healthcare or finance. Therefore, protecting sensitive information requires robust systems designed to address today’s challenges. Strong privacy compliance and adherence to data protection laws are essential in these workflows
The solution is specialized workflows that prioritize protection without compromising quality. Technical security tools and automated checks help teams maintain accuracy and minimize risks. This approach simplifies compliance with different legal standards in different regions. By ensuring CCPA compliance and following international privacy frameworks, organizations navigate regulatory requirements more effectively.
Quick Take
- Hands-off processing systems reduce vulnerabilities in sensitive workflows.
- Cross-industry standards, such as HIPAA, require customized security strategies.
- Automated quality checks support accuracy and enhance security.
- Unified systems facilitate navigation of compliance requirements across multiple regions.

Understanding the “privacy rules of annotation data
Raw information comes in many forms. Emails and documents feed text models. Visual systems rely on images and videos. Sensor data, such as GPS coordinates or temperature readings, requires special processing. Audio files encompass a wide range of content, from speech to environmental sounds. Applying privacy frameworks and following annotation governance principles ensures that data sovereignty and regulatory requirements are respected at every stage.
Why Compliance Matters
Security is about blocking unauthorized access attempts. Privacy ensures that people have control over their information. This is important when processing medical records or financial data. A single breach can lead to lawsuits and undermine customer trust. Maintaining privacy compliance and adherence to international privacy and data protection laws is critical to avoid regulatory penalties.
Automated quality checks help maintain accuracy and protect sensitive materials. Proper workflows protect both organizations and individuals. Fines for non-compliance often exceed $1 million for violations in regulated industries.
Legal and Regulatory Framework for Data Annotation
The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) outlines the rules governing the processing of personal data. Organisations must obtain explicit consent and allow individuals to delete or correct their information.
In healthcare, HIPAA mandates the encryption of medical records and restricts access to them to authorized personnel only. Teams working with patient data must only have access to what is necessary to perform specific tasks.
California’s CCPA gives residents control over their digital footprint. Companies must disclose the information they collect and allow users to opt out of sharing information with third-party organisations. This has implications for annotation workflows that include tracking consumer behaviour.
Integrating international privacy standards and privacy frameworks ensures that annotation governance aligns with regulatory requirements.
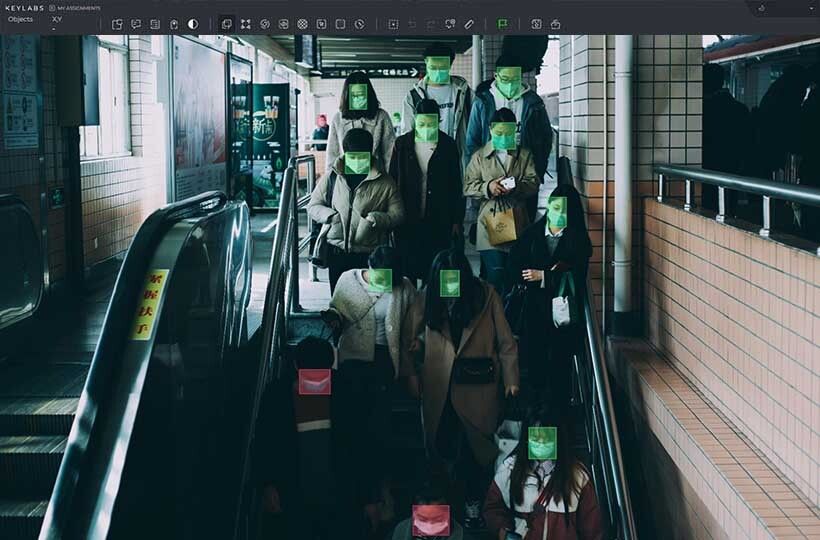
International standards and their role
ISO 27001 provides a framework for protecting sensitive information across various industries. Its 114 controls cover encryption, access management, and incident response. The certification demonstrates a commitment to protecting user data throughout the labeling process.
Keymakr is fully compliant with data protection and privacy requirements. The company is certified to ISO 9001: Quality Management System and ISO 27001: Information Security. This confirms a high level of process control and data protection for customers.
The company's processes also comply with GDPR and HIPAA requirements, which guarantee the secure handling of personal and health data. Compliance with the CCPA demonstrates transparency in the collection and use of user data. Additionally, staff receive ongoing training in cyber hygiene and privacy, ensuring that they handle annotated datasets responsibly.
These standards ensure the reliability of all stages of data annotation, from storage and access to quality assurance and scaling processes on the Keylabs platform.
Data Annotation Security Practices
Data annotation security practices encompass technical, organizational, and procedural measures designed to protect the confidentiality of information.
All data is encrypted at multiple levels during transmission and storage to prevent unauthorized access. Each employee has personal access rights that restrict unauthorized individuals from viewing or editing sensitive information. Regular security reviews, log audits, and user activity monitoring allow for the rapid detection and remediation of potential breaches.
Data anonymization and pseudonymization are used to increase the reliability of processes. This occurs when personal identifiers are replaced with neutral labels, thereby reducing the risk of identity disclosure.
Continuous improvement cycles
Continuous improvement cycles are a crucial data annotation security practice because they ensure that processes, policies, and tools are systematically updated to reflect new risks and technological advancements. They regularly monitor the effectiveness of security measures, analyze incidents, check compliance with privacy standards, and implement corrective actions. Continuous staff training, audit of internal procedures, and implementation of feedback from the annotation team help to identify vulnerabilities in a timely manner and increase the level of data protection. This approach fosters a security culture where each stage of data processing is thoroughly reviewed, and all changes are designed to enhance reliability and compliance with regulatory requirements.
User consent and transparency in annotation
Ensuring user consent and transparency in annotation requires that any information collected for annotation purposes is used only after obtaining clear, informed, and voluntary consent from the data owners. Informed consent means that users have a full understanding of what data will be collected, how it will be processed, for what purpose, for how long, and who will have access to it. Transparency involves keeping users informed through clear messages and data management tools that allow them to control the use of their information.
Users should be able to withdraw their consent at any time and request the deletion of their data from the system. This approach ensures compliance with legal requirements and creates a culture of trust between the company and users.
Risk Management: Data Leaks and Privacy Issues
Risk management in data annotation is essential to prevent information leaks and protect user privacy. Identifying potential threats and implementing practical solutions helps minimize negative impacts on the business and users.
FAQ
How do regulations like GDPR impact AI training datasets?
These regulations affect AI training datasets by restricting the collection and use of personal information, requiring informed consent, and safeguarding user privacy.
What security frameworks are in place for healthcare annotation projects?
Healthcare annotation projects employ security frameworks that include data encryption, access control, patient anonymization, and compliance with HIPAA and GDPR standards.
How to balance model accuracy with the need for anonymization?
Model accuracy can be aligned with anonymization requirements by applying pseudonymization and data aggregation techniques that preserve features useful for training while keeping personal information confidential.
Are voice recordings treated differently under COPPA?
Under COPPA, voice recordings containing personal information of children are considered sensitive data and are subject to strict parental consent requirements.