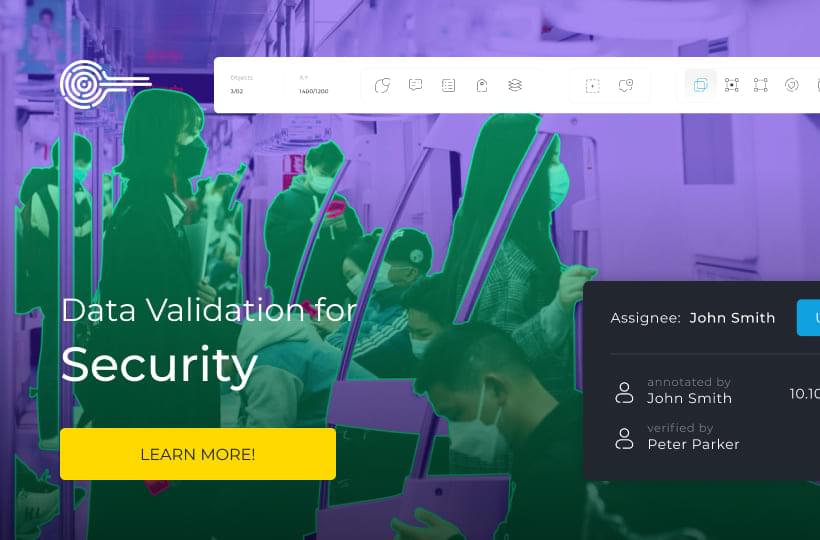
Implementing Semi-Automated Labeling: Balancing Speed and Accuracy
Balancing speed and accuracy is important in machine learning and data annotation. Semi-automatic labeling settings combine AI's speed with human control's accuracy. This method speeds up labeling while preserving data quality for robust AI models.
Human annotators are required for the manual labeling of complex data. They maintain the accuracy of anomaly detection. A semi-automatic approach uses artificial intelligence to pre-label, which is then processed by annotators for better accuracy. Semi-automatic labeling settings offer speed and consistency.
Quick Take
- Semi-automatic labeling combines the speed of automation with the accuracy of annotators.
- Manual annotation is suitable for complex, context-rich tasks but is time-consuming and expensive.
- Automated labeling is fast, scalable, and ideal for large data sets but has problems understanding nuances.
- Semi-automatic methods provide a balance for high-quality data labeling.

Understanding Semi-Automated Labeling Setups
Partial labeling is a process that uses automated methods and human intervention to label data. This can simplify the labeling process for large amounts of data.
Applications in Various Industries
Semi-automatic labeling provides consistent labeling across multiple industries.
- Medical diagnostics. Semi-automatic labeling analyzes medical images. AI models can automatically detect abnormalities, and doctors can verify these diagnoses.
- Image processing for autopilot systems to recognize objects on the road, such as pedestrians, other vehicles, signs, and road obstacles.
- Finance. Semi-automatic labeling marks suspicious transactions in financial data. Algorithms identify fraudulent transactions, and annotators review them for confirmation.
- Manufacturing. Quality control of products, such as damage or incorrect dimensions, followed by inspection by a specialist.
- Marketing. Analyzing user behavior on websites and mobile apps to adapt marketing campaigns.
Manual vs. Automated Labeling
Manual annotation relies on human intelligence. This approach is accurate but slow and expensive. Automated labeling using machine learning is faster and cheaper but less accurate. This shows the need for hybrid solutions. More details on this topic in the blog Keylabs.
The Rise of Semi-automation
Semi-automated labeling combines human verification with artificial intelligence data processing. This approach increases productivity by reducing the workload on annotators. AI algorithms are used for the initial labeling.
Benefits of Partial Labeling
- Speed and accuracy. Combining automation with human control allows for fast and accurate processing of large amounts of data.
- Cost-effectiveness. Reducing the need for manual labeling saves resources and reduces labor costs.
- Wide range of applications. Used in various industries - from medicine to industry and security.
- Scalability. Semi-automatic labeling easily adapts to processing large amounts of data.
- Better quality of training AI models. Accurate labels improve the quality of training machine learning algorithms.
- Ease of verification. Annotators quickly detect errors in automatic labeling.
- Adaptation to new data. Ability to quickly update labeled datasets with new samples or changes in the data structure.
Challenges in Implementation
One technical challenge when implementing semi-automated labeling is ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure. This may include integrating existing data management systems, databases, analytics platforms, etc.
Some tools may require modifications or additional components to work correctly. This can increase costs and the time needed for implementation.
Staff Training and Transition
Implementing semi-automated labeling requires staff to adapt to new working conditions. This can be problematic if employees use manual methods or have limited experience with the latest technologies.
The human aspect of the transition to semi-automated systems is important. Companies must invest in training annotators to work correctly and quickly with advanced systems in the future. Combining tools with training staff is important to ensure they see things correctly.
Despite the skills gap, progress in semi-automated data annotation software is promising.
Solving these problems leads to an accurate labeling process.

Practices for Successful Implementation
Planning when setting up semi-automated labeling systems seamlessly integrates labeling automation tools. Key planning considerations include:
- Defining goals and objectives.
- Analyzing needs.
- Selecting the right data annotation software.
- Integrating quality assurance mechanisms.
Maintenance and Support
Key Performance Indicators
Evaluating machine learning data labeling speed is measuring and analyzing the speed at which data is labeled for machine learning models.
Evaluating data labeling speed includes:
- Labeling throughput measures the number of items labeled per hour.
- The time it takes for the model to predict labels.
- The time it takes to complete a labeling task from start to finish.
Metrics for Accuracy
Accuracy metrics support standards for machine learning, as well as human intervention:
- The error rate is the percentage of incorrect labels assigned.
- The consistency of labeling across multiple annotators and machine predictions.
- The quality score combines metrics such as precision, recall, and F1 score to assess labeling quality comprehensively.
The F1 score measures the quality of a machine learning model, which is used to assess its classification accuracy.
Companies can track their progress using the following KPIs:
- Monthly sales growth.
- Average profit margin.
- Revenue per customer.
- Customer satisfaction index.
- Customer loyalty and retention rate.
These KPIs are the path to success for companies looking to optimize their operations.
Future Trends in Labeling Technologies
Marking technologies are evolving through innovations in automation and artificial intelligence.
Integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning will use deep learning algorithms for automatic object recognition and classification.
Marking accuracy will increase through self-learning AI models.
Predicting marking errors and their automatic correction will also be improved.
The creation and development of innovative marking systems will allow them to automatically adjust marking parameters based on the analysis of input data. Intelligent sensors and cameras will allow for the accurate assessment and control of the quality of data annotation.
Data analytics and monitoring large volumes of data to detect anomalies and optimize data marking processes.
Forecasting the need for technical re-equipment based on the analysis of performance indicators.
The future of marking technologies is aimed at automation and intelligent systems. Combining AI will create accurate, reliable, and energy-efficient solutions that meet the requirements of production and logistics.
FAQ
What is a semi-automated labeling?
Semi-automatic labeling is a process that uses automated methods and human intervention to label data. This can simplify the labeling process for large amounts of data.
What challenges might we face when implementing semi-automated labeling systems?
Challenges include technical limitations, such as compatibility with existing packaging lines. Bespoke adjustments may be needed. Adequate staff training is also essential for a smooth transition.
How do you choose the semi-automated labeling setup for needs?
You must consider the product type, production volume, and labeling accuracy requirements. You also need to ensure compatibility with your current infrastructure and the ability to automate processes.
What are the practices for implementing semi-automated labeling systems?
Successful implementation requires strategic planning and thorough consideration of the production environment and goals. Continuous maintenance and support are critical for addressing emerging challenges and ensuring peak efficiency.
What key performance indicators should we monitor in semi-automated labeling systems?
Important KPIs include metrics for speed and accuracy. Monitoring these metrics helps quantify the impact of semi-automation technology. It ensures the systems deliver expected improvements in efficiency and data quality.
What future trends are expected in labeling technologies?
The future of marking technologies is aimed at automation and intelligent systems. Combining AI will create accurate, reliable, and energy-efficient solutions that meet the requirements of production and logistics.