Interpolating Objects in Video Annotations
Working with moving video presents unique challenges for data annotator teams. This task is time-consuming when you need to label features across hundreds or thousands of individual images. Manual approaches produce inconsistent results and slow down projects.
Intelligent algorithms can speed up manual work. The method involves manually labeling only a few key moments. The system then automatically applies these labels to all surrounding frames.
Quick Take
- Manually labeling sequential images is slow and prone to inconsistencies.
- Intelligent algorithms can automatically extend labels across multiple frames, providing significant video labeling acceleration.
- High-quality training data is essential for building robust AI models.
- This method maintains accuracy while significantly speeding up the workflow.

Understanding Video Annotations in AI
Video annotation in AI involves the AI learning to recognize and interpret events, objects, and actions in videos based on structured labels created by annotators.
These labels provide crucial context that enables AI systems to interpret visual information accurately and effectively. High-quality annotated data forms the basis of robust AI models.
Annotations come in a variety of formats to meet different needs. Common types include bounding boxes that outline features, polygons for shapes, and key points for landmarks.
In autonomous driving systems, this labeling helps vehicles identify pedestrians and road signs. Surveillance systems use annotated video footage to track movement and detect unusual activity.
The goal goes beyond simple tagging. It's about creating rich, informative datasets that allow algorithms to learn complex patterns.
What is object interpolation in video annotation?
Object interpolation commonly referred to as frame interpolation, is the process of automatically filling in intermediate object positions between manually labeled frames. When an annotator marks an object in the start and end frames, the video annotation system utilizes computer vision algorithms to predict the object's location in all the frames in between. This reduces manual work, speeds up the annotation process, and improves the consistency of the annotation, especially for dynamic scenes.
Interpolation can account for the trajectory, speed, size, and orientation of the object, making the annotation more accurate and suitable for use in training AI models for motion tracking or video analytics systems.
Interpolation Methods and Algorithms
Several interpolation methods and algorithms vary in complexity, accuracy, and applicability in different scenarios, depending on the scope of application.
Selecting and refining keyframes for accurate annotation
Frame selection is the foundation of accurate automated labeling processes. Selecting the optimal moments for keyframe annotation has a significant impact on the quality of the final dataset.This ensures smooth transitions between annotated frames.
Criteria for selecting keyframes
Identify frames where elements undergo vigorous transformations. Pay attention to changes in position, size, or appearance. These moments have reference points.
Select frames that represent maximum motion. This helps capture complete trajectories. Regular intervals between keyframes ensure consistency.
Pay attention to complex transitions and overlapping elements. These situations require manual annotation or correction. Proper placement of keyframes prevents tracking errors throughout the sequence.
Handling complex object motions
Some motions can hinder standard automation. Rapid changes in direction and overlaps require special handling. Additional reference frames often solve these problems.
When elements move unpredictably, increase the keyframe rate to maintain smooth animation. This provides more points of reference for the system. Iterative refinement helps correct any remaining inaccuracies.
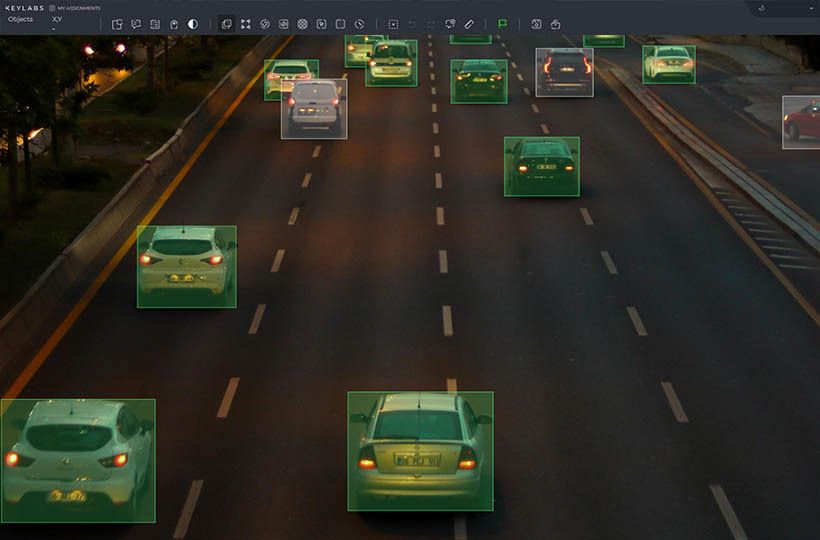
Combining interpolation with object tracking
These two methods create a synergy that improves sequential data processing.
Automatic frame prediction reduces the initial workload. It creates a solid foundation by marking intermediate images between key moments.
Intelligent motion analysis builds on this foundation. Advanced systems analyze visual characteristics and adjust marks as elements move sequentially, improving temporal consistency throughout the sequence.. This combination corrects common prediction errors. When elements change shape or temporarily disappear, tracking models maintain accuracy. A hybrid approach handles complex scenarios that either method alone might miss.
Modern platforms, such as Keylabs, combine both methods. Prediction handles regular motion patterns, while tracking resolves complex motions. Teams of experts process large data sets and maintain quality standards.
The main advantage is in the strategic allocation of resources. Specialists focus on complex decision-making moments, not on repetitive tasks.
Fixing automatic interpolation errors
When working with sequential images, occasional errors can occur during the automatic processing phase. These errors do not mean that the technology has failed, but rather indicate where human experience can improve the result.
- Preview interpolated frames. Check the results of automatic interpolation for apparent errors, such as object displacement, disappearance, incorrect scale, or orientation.
- Identify problem frames. Mark frames where the object trajectory is erroneous, or the movement looks unnatural.
- Manually adjust key frames. Move, scale, or correct the position of the object at critical frames.
- Re-interpolate. Rerun the interpolation algorithm after making corrections so that the system incorporates the new key points.
- Check the smoothness and accuracy of the movement. Assess whether the trajectory has become natural and whether the object movement matches the dynamics of the scene.
- Final validation and approval. Preparing the annotation for use in training AI models or analytical systems.
Evaluating Video Annotation Tools and Platforms
The market offers a variety of solutions for working with moving images, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages.
Basic evaluation criteria include the following aspects: how intuitive the tool is for annotating moving objects, what automation mechanisms it offers, how large video streams are processed, whether teamwork with task distribution is supported, the breadth of data format support, and how the project management system is designed.
Different solutions may include automatic interpolation algorithms, tools for working with key frames, opportunities for integration with machine learning models, mechanisms for assessing annotation quality, and metadata management.
When choosing, it is worth considering whether the platform supports collaborative work among a group of annotators, how easy it is to organize workflows and data validation, and whether it offers advanced capabilities for processing large volumes of video without compromising speed and accuracy.
One such solution is Keylabs, a modern video and data annotation platform focused on preparing data for machine learning. Keylabs offers tools with support for automatic functions, including algorithms for interpolating objects between key frames. The platform provides advanced project management capabilities, including task allocation, progress tracking, and integration with ML processes, which simplifies teamwork on large data sets.
Application options in different industries
Video annotations are a crucial tool for data preparation in various areas where the accurate processing of moving objects is essential. They enable the training of artificial intelligence models to track, analyze, and predict the behavior of objects in video. Let's examine the primary application options across various industries.
FAQ
How does this method speed up the labeling process?
This method automatically fills in the gaps between keyframes.
What is the difference between tracking and interpolation?
Tracking determines the actual position of an object in each frame of video, while interpolation predicts its position between manually annotated frames.
How is this technology used in real-world applications?
Video annotation technology is used in real-world applications to accurately track and analyze moving objects in sports, autonomous transportation, security, healthcare, and media systems.
What happens if automatic labeling makes a mistake?
If automatic labeling makes a mistake, it can lead to inaccuracies in the data, which in turn can reduce the efficiency and accuracy of the trained AI model.