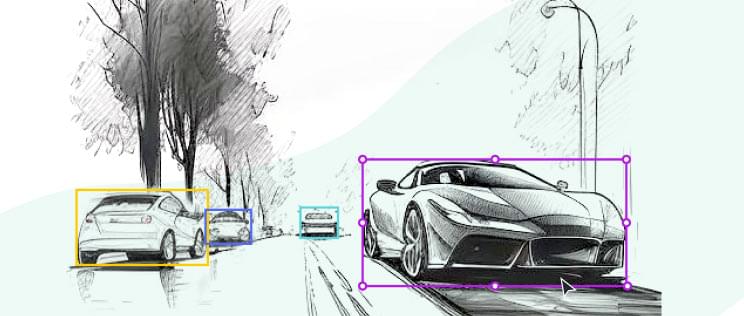
Image annotation tool
Keylabs: precision meets innovation in image annotation.
Our platform, born from extensive experience and a deep understanding of the industry's needs, bridges the gap in data annotation with unparalleled 99,9% precision.
Keylabs uniquely blends AI tools with adaptability, allowing seamless integration of any client model for specific project demands. The annotation process includes exclusive post-annotation features like Edge Smooth and Healer Tools, enhancing precision and efficiency.
Image annotation types
Keylabs makes image annotation easier for AI developers. Our platform features every image annotation type and technique.This offers developers a large degree of flexibility. Keylabs can craft datasets that meet the needs of any AI project.Image segmentation is an important part of dataset construction:
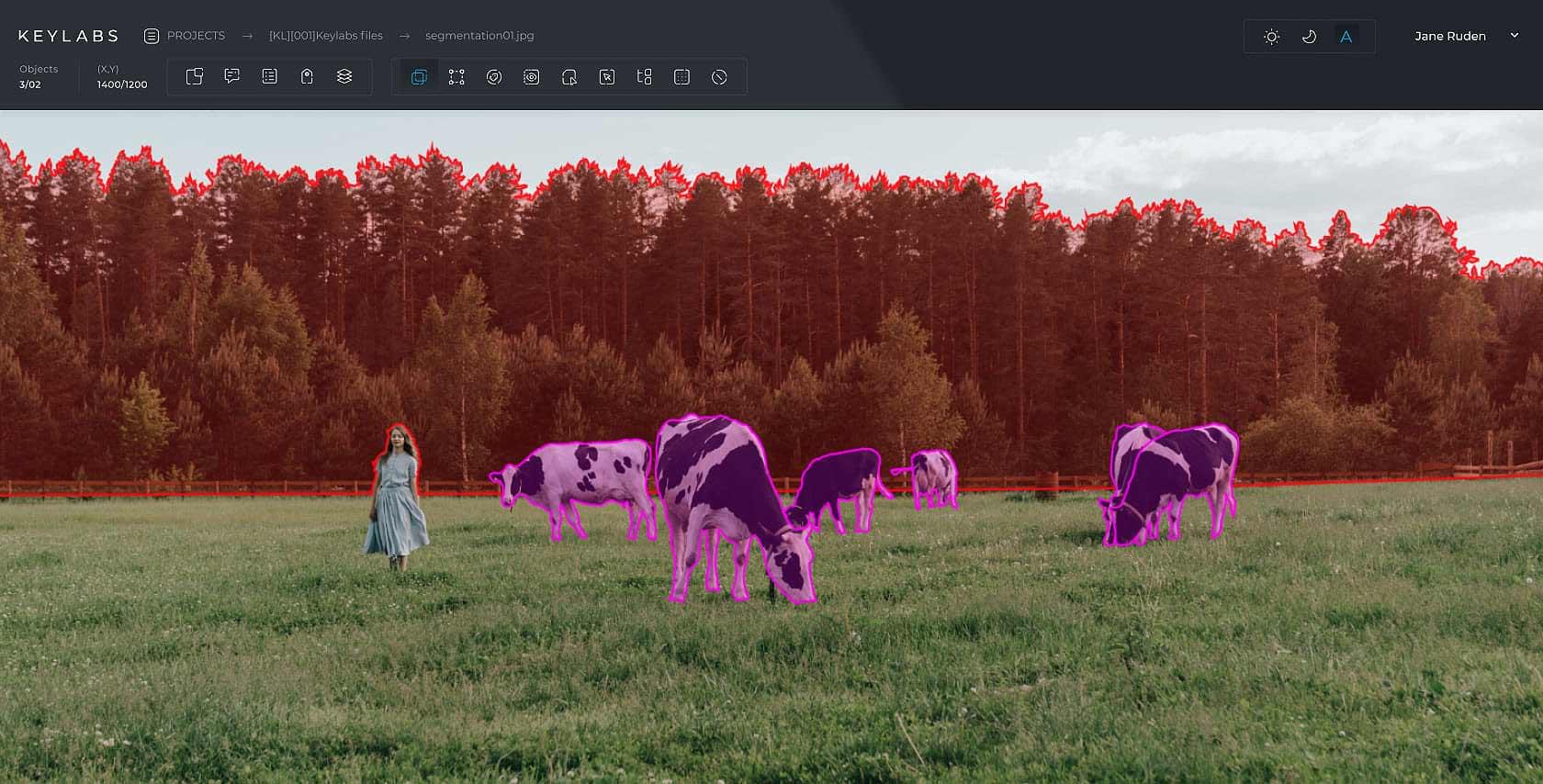
Semantic segmentation
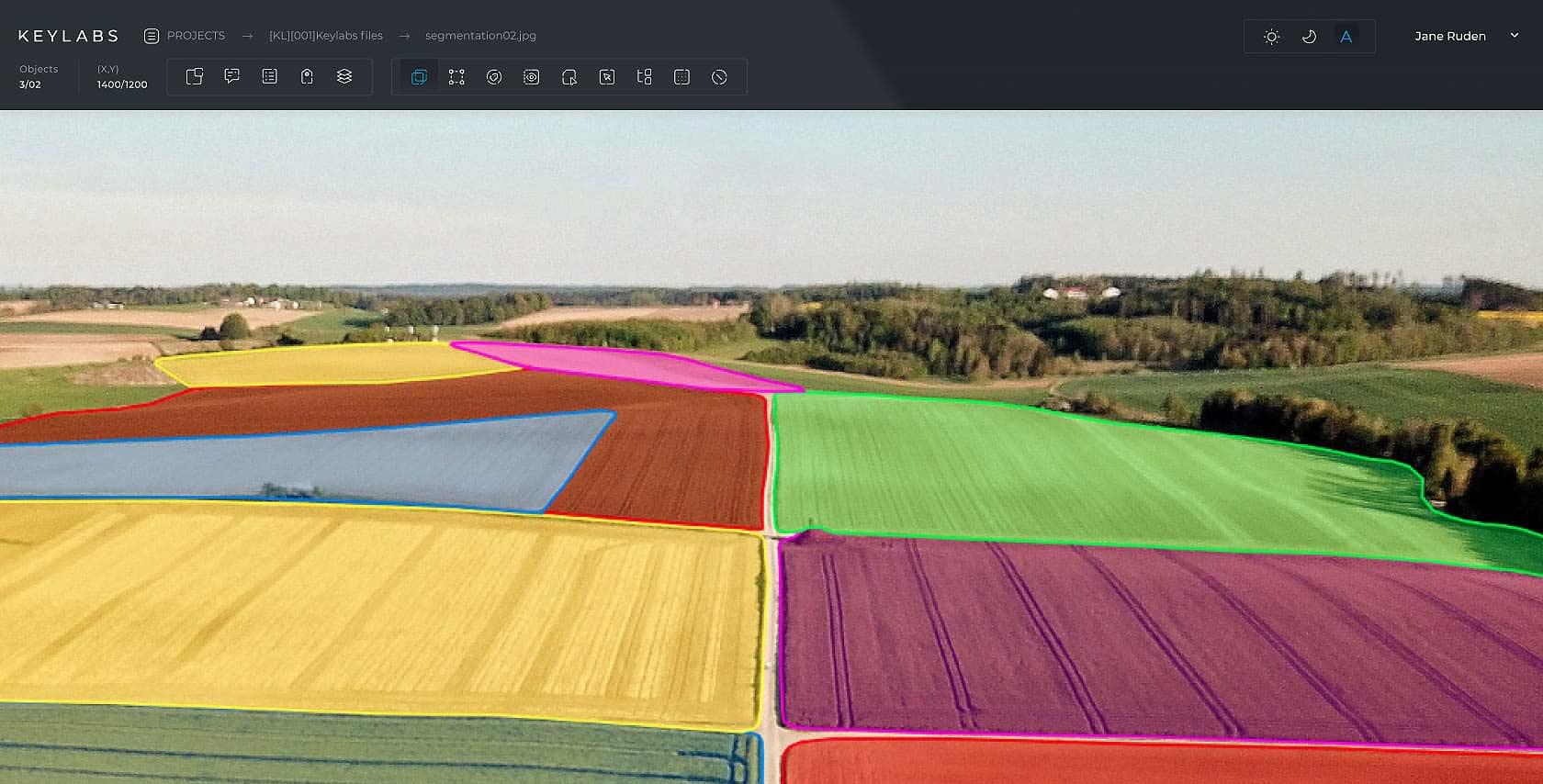
This is the most commonly used form of image segmentation. It involves separating each pixel in an image into classes and then labeling them.Annotators use a polygon annotation tool to outline objects so that they can accurately capture their shape. Any background features, like sky or trees, are also assigned labels and highlighted. This means that every pixel in the image is connected to a label.
Instance segmentation
The annotation type adds further granularity to images. Whereas semantic segmentation assigns every occurrence of an object to the same class, instance segmentation identifies each time an object occurs. When there are more than one of the same object in an image then both will be given their own label and highlight colour. By doing this it is possible to further enrich image training data.
Image annotation techniques
Keylabs is an image annotation platform that features every labeling technique. AI companies can use this range of techniques to construct training image data that fits the needs of their models. Competitive image annotation tool pricing also makes Keylabs an attractive choice for AI developers. The following techniques can be used to power a huge number of AI applications:
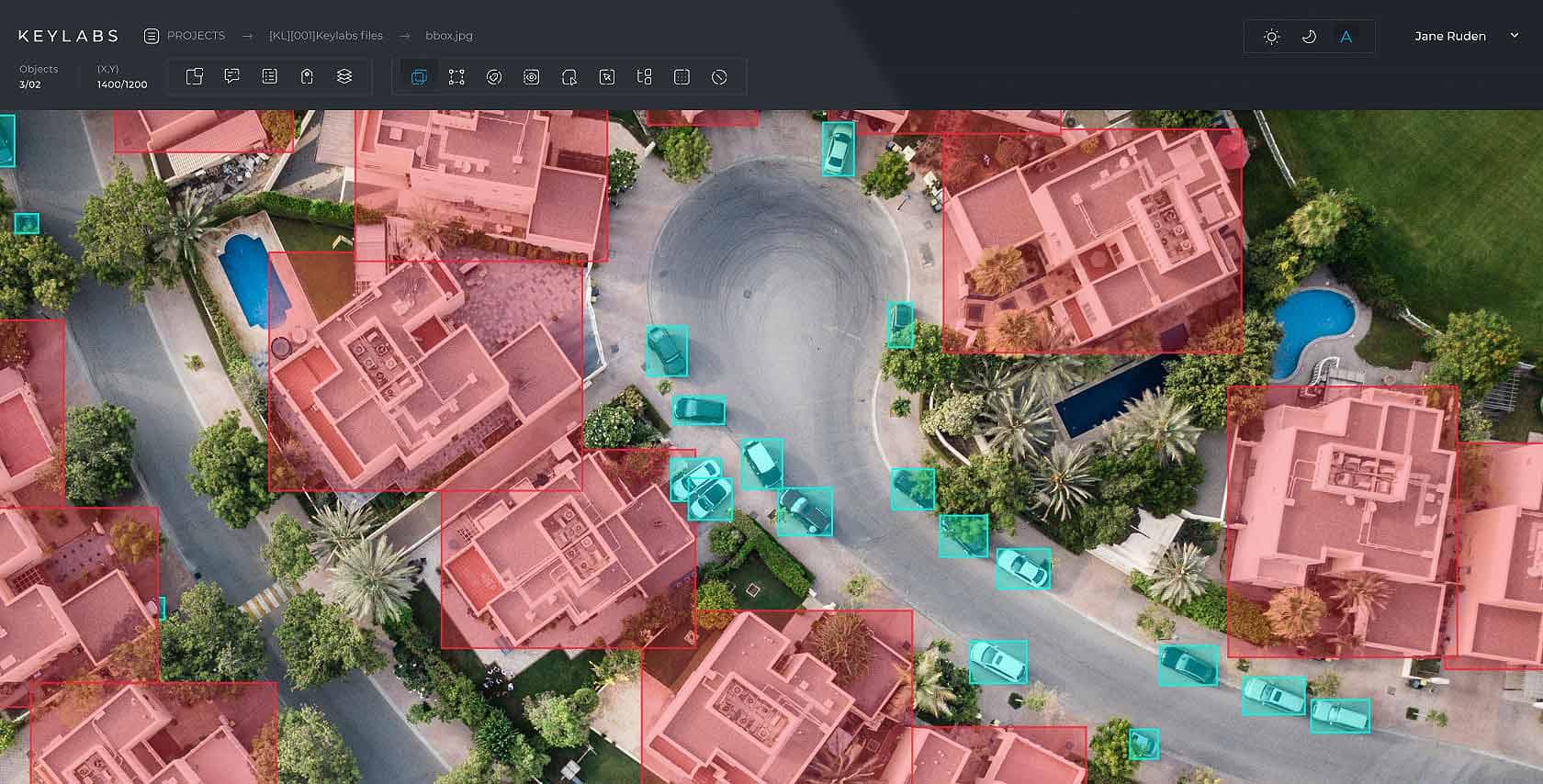
Bounding box
This is the most common annotation type. Using the Keylabs image annotation tool annotators drag boxes around targeted objects. This technique is quick and simple. However, it does not capture as much detail as other methods.
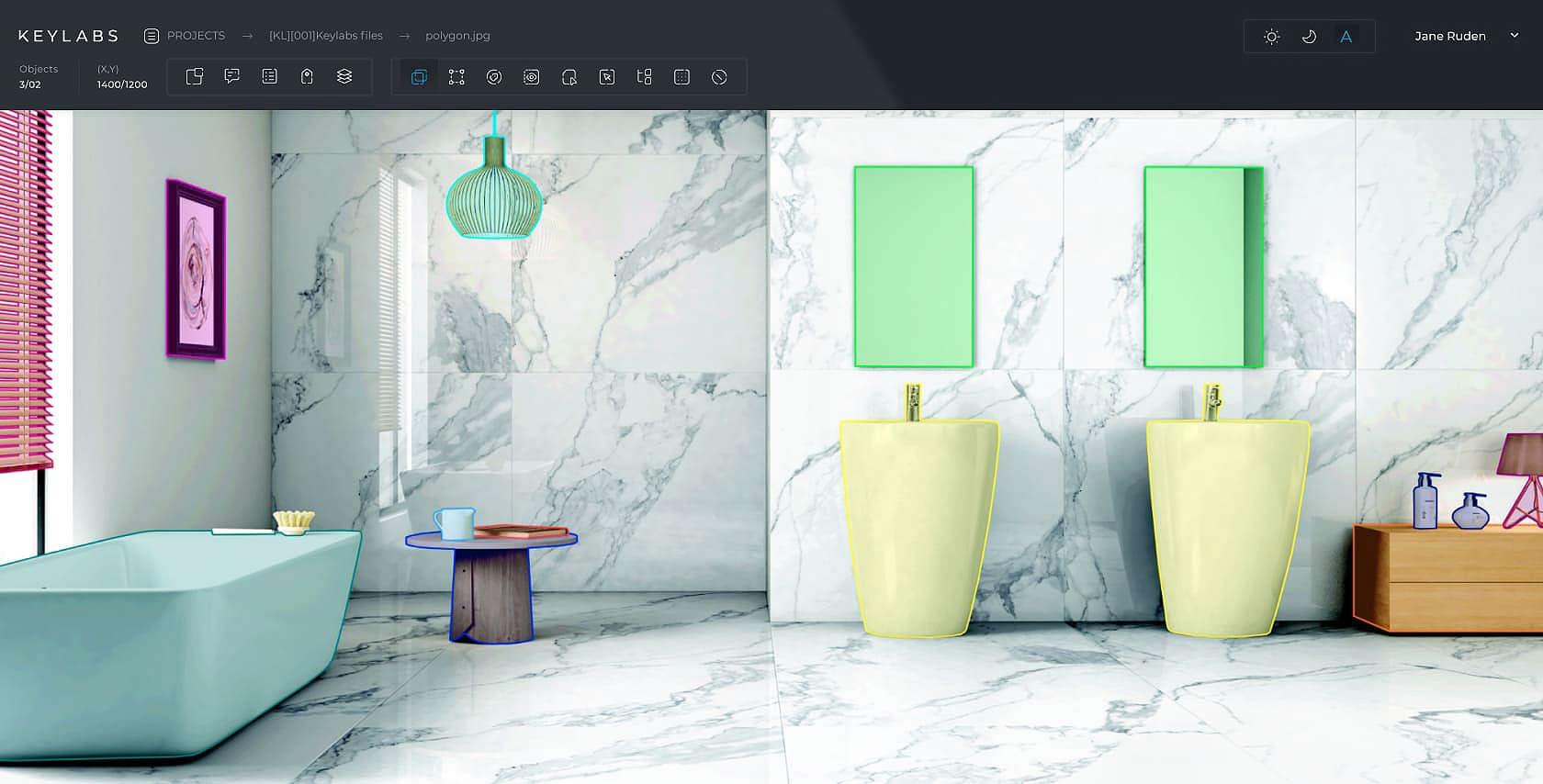
Polygon
The Keylabs platform allows annotators to outline complex shapes. By connecting small lines around an object annotators can precisely define its shape. This process is known as polygon annotation.
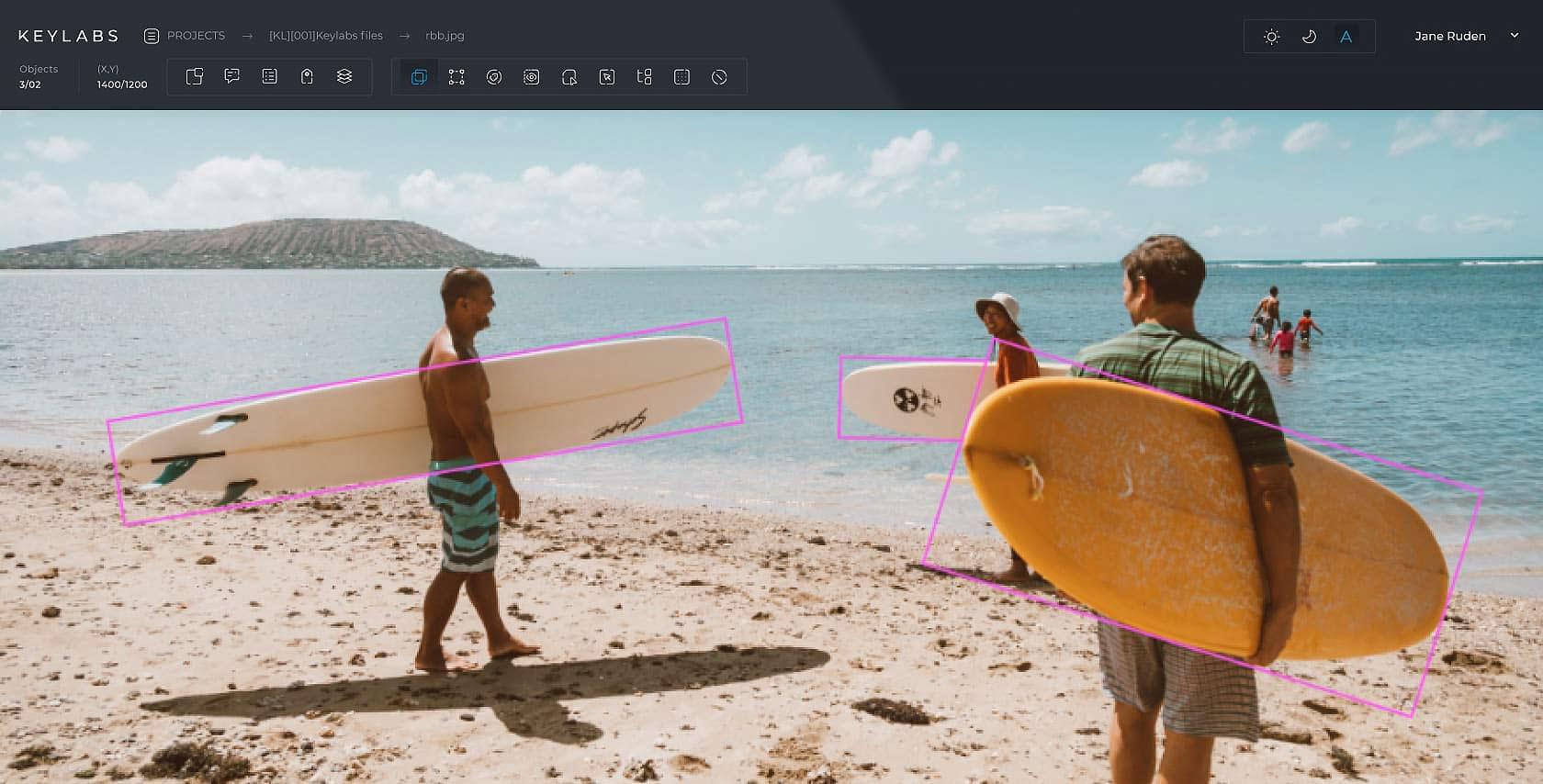
Rotating bounding box
In the image data annotation process, the rotating bounding boxes tool provides a way to more accurately encapsulate objects that aren't aligned with the horizontal or vertical axes of the image. By allowing the bounding box to rotate around its center, the annotation can closely match the orientation of the object, ensuring more precision in datasets, especially for tasks like object detection where the object's orientation matters. This approach minimizes the unnecessary background within the bounding box tool, enhancing the accuracy of machine learning models trained on such annotated data.
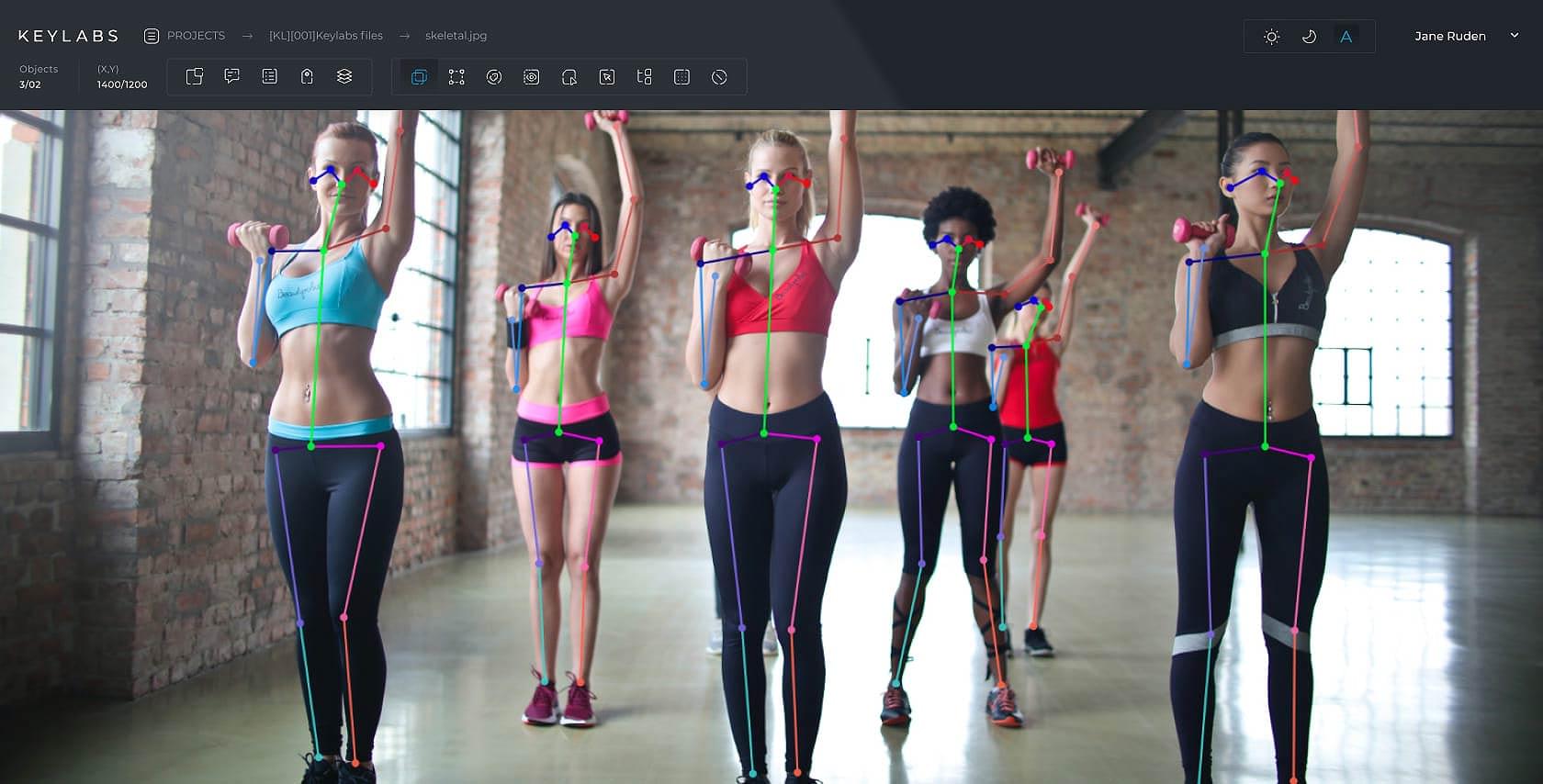
Skeletal
Many AI applications are designed to interpret human bodies. Skeletal annotation trains AI models to do this. Annotation tools allow annotators to attach lines to images of humans, locating limb positions and body shapes.
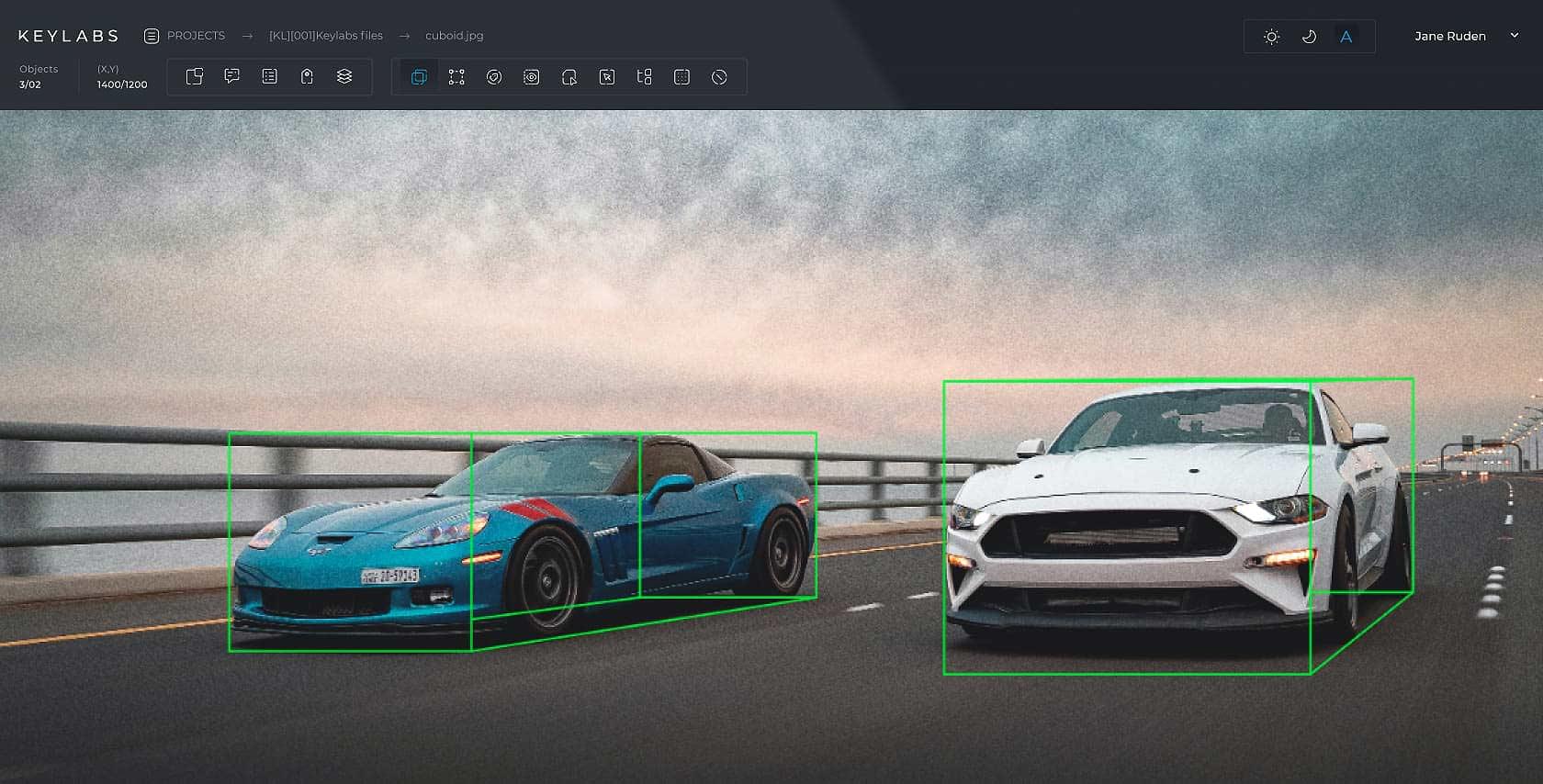
Cuboid
Cuboid data annotation tools enable the representation of objects in images with three-dimensional properties, capturing depth, width and height within a two-dimensional space. These data annotation tools place 3D bounding boxes, or cuboids, around objects, providing a richer spatial understanding compared to traditional 2D bounding boxes. Primarily employed in autonomous driving and augmented reality applications, cuboid annotations give computer vision models a nuanced understanding of object placement and scale within a scene.
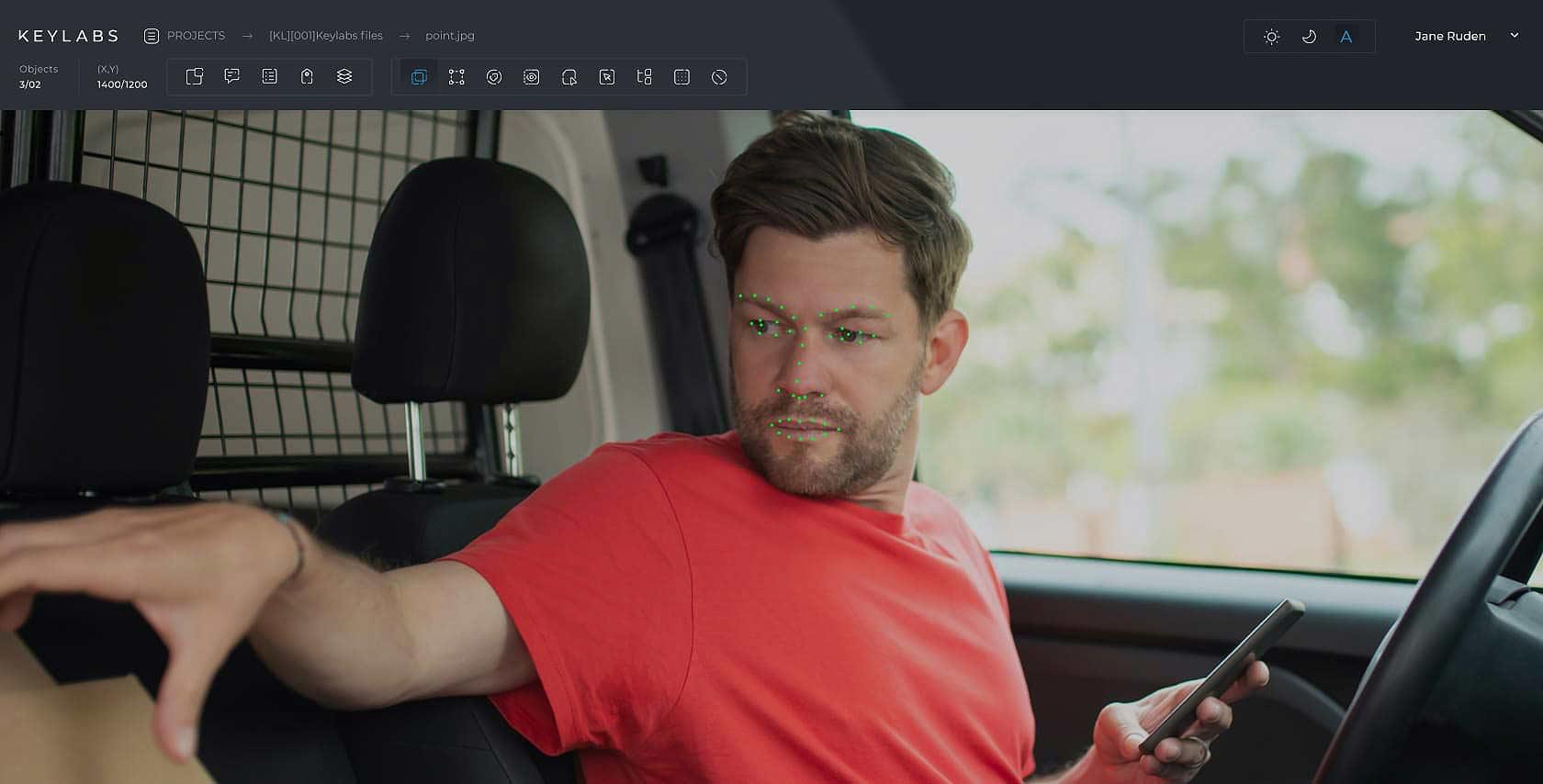
Key points annotation
This technique uses points to locate important features. One common example of key point annotation is facial feature labeling, where points are used to identify noses, eyes, lips, etc.
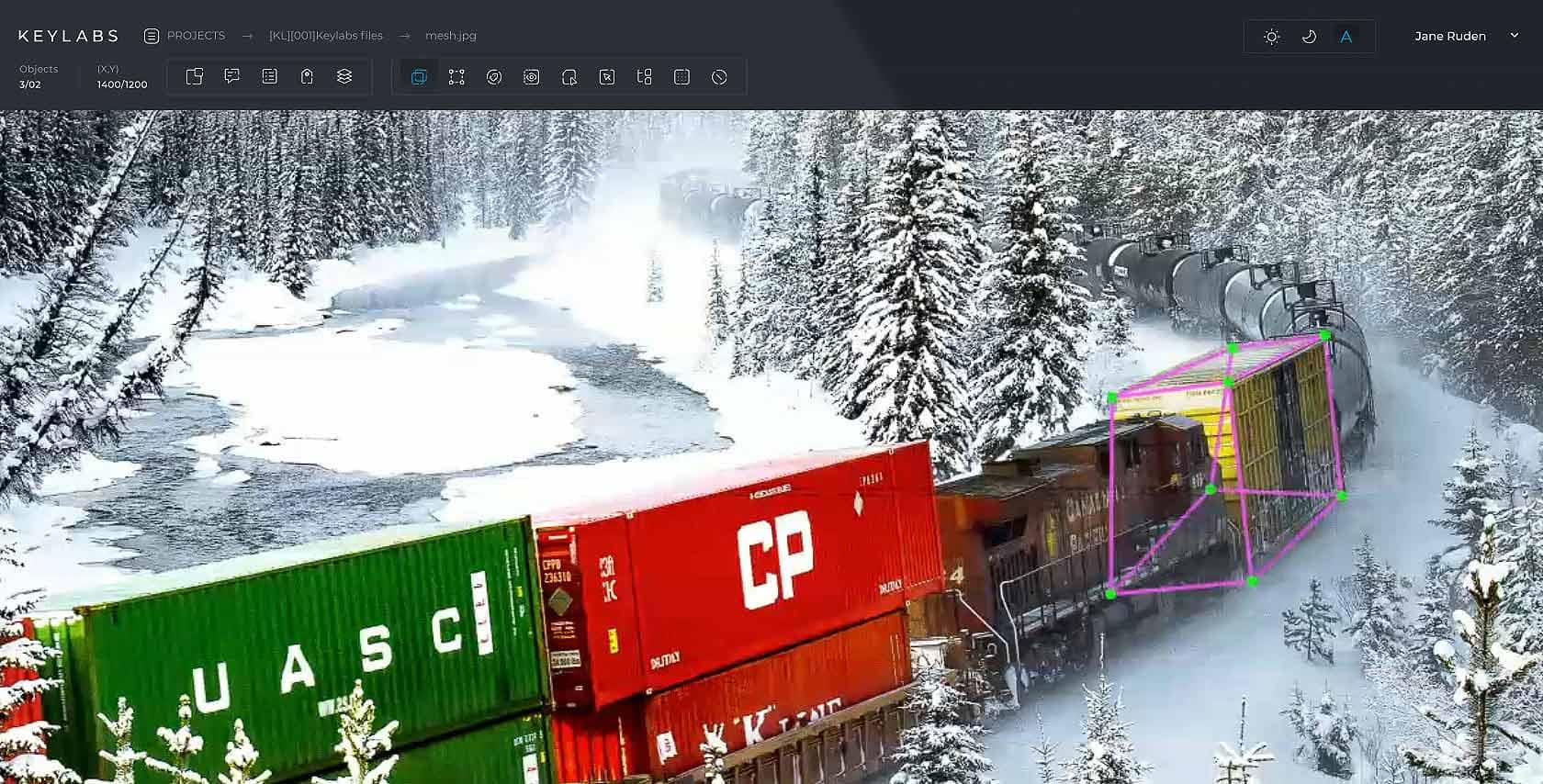
Mesh
Mesh data annotation tools are instrumental in creating intricate, polygonal representations of objects within images or 3D spaces. Unlike traditional annotation methods, these tools plot vertices and edges to form a dense mesh, encapsulating the nuanced contours and surfaces of an object. Widely used in 3D modeling and advanced computer vision tasks, mesh annotations capture the complex geometric and topological characteristics of objects.
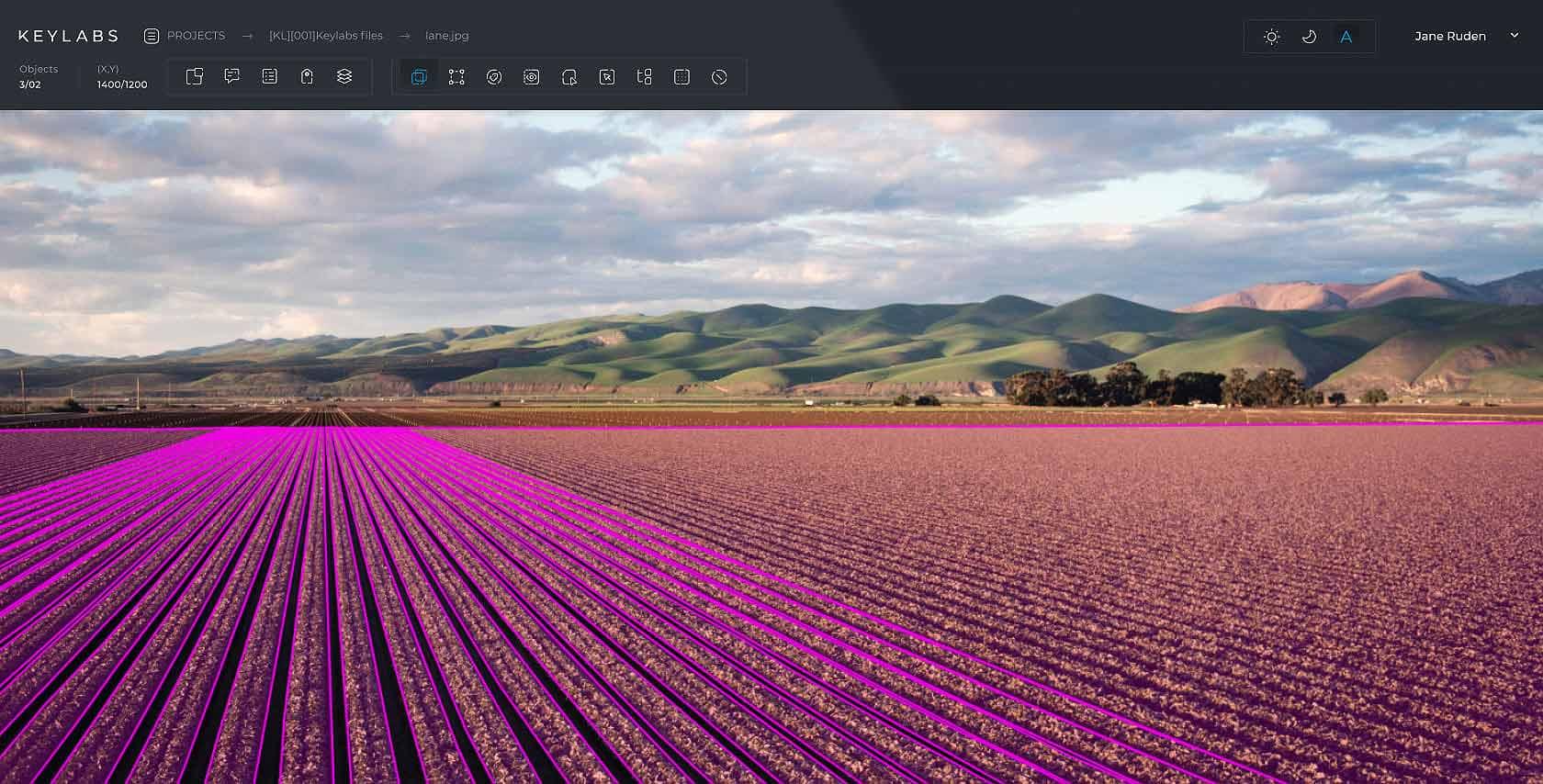
Lane annotation
This annotation technique is primarily used to identify roads, railway lines, pipelines and other linear structures. Annotators trace the shape of these features using annotation platform tools.
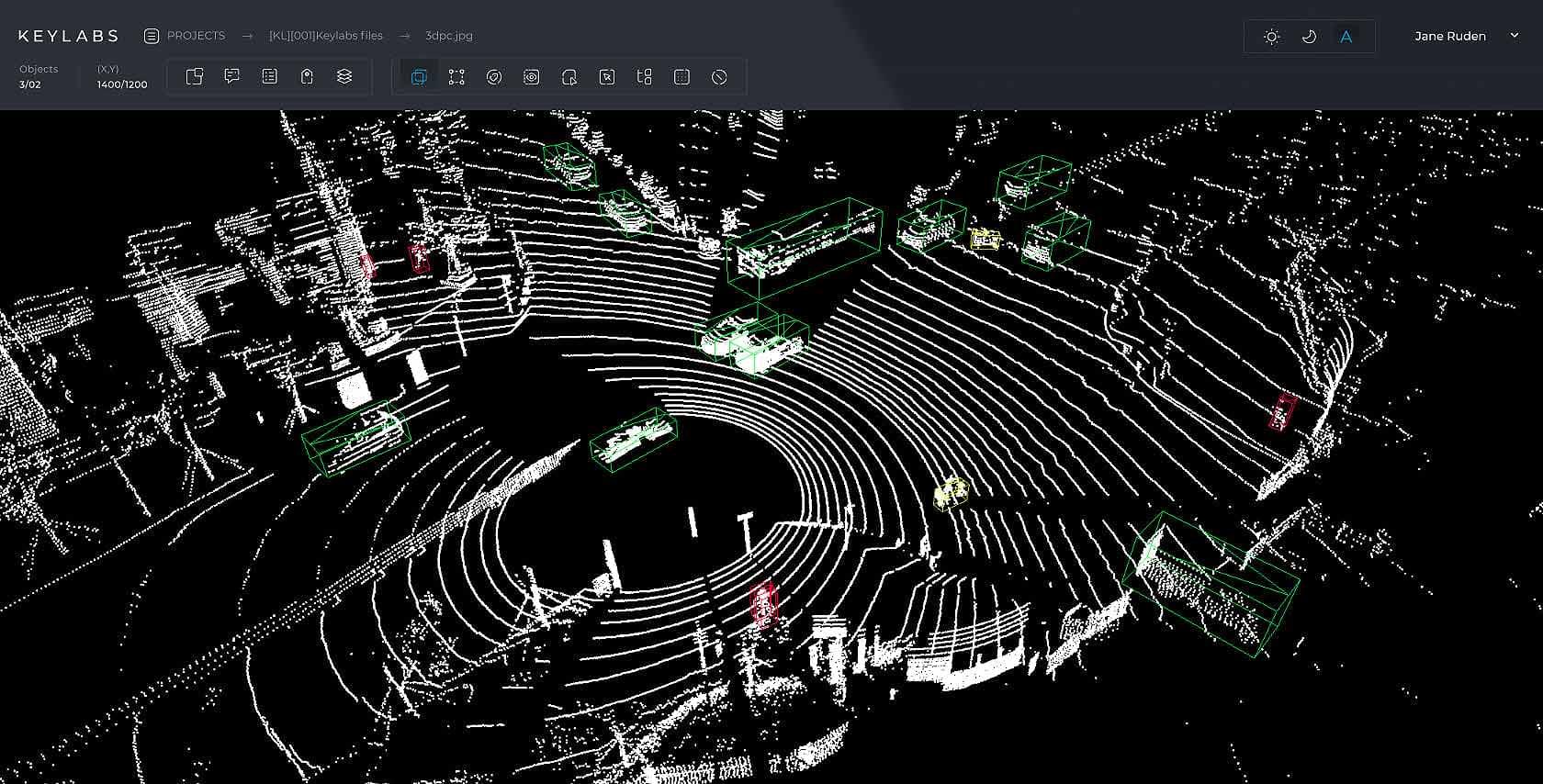
3D point cloud
A 3D point cloud is considered to be a more complex type of annotation, because it is already about 3D. From some types of cameras, information comes in three-dimensional scanning of space and not in the form of videos and pictures. Basically, we are now talking about Lidar - this is a radar, a device that receives a three-dimensional description of objects. This is a slightly more complex annotation level.

Bitmask
This annotation type links individual pixels to specific objects, allowing for annotations that are separated or contain gaps.

Custom annotation
All of the above annotation techniques can be combined to accomplish specific annotation goals. Keylabs image annotation platform online gives AI companies flexibility and options when planning annotation projects.
Industries we serve
Keylabs is created as a platform that incorporates state-of-the-art, performance oriented and user friendly annotation tools with built in machine learning and operation management capabilities.
Keylabs: a powerful tool for image annotation
Quality results from a team of annotation experts
Tap into decades of annotation experience from the team that created the Keylabs image annotation tool.
Image annotation tool pricing
Keylabs offers competitive image annotation tool pricing for AI developers. Choose a smaller flexible package or take advantage of our volume based discounts. In our demo call we evaluate the needs of your project and identify the pricing options that are right for you.

Start Free Trial
Transparent Plans & Prcing with No Hidden Fees!