Waste management
Keylabs' precision annotation: driving efficiency in waste management AI.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of modern society, as we strive to minimize our impact on the environment and create a sustainable future. But managing waste effectively requires accurate data, which can be challenging to collect and analyze.
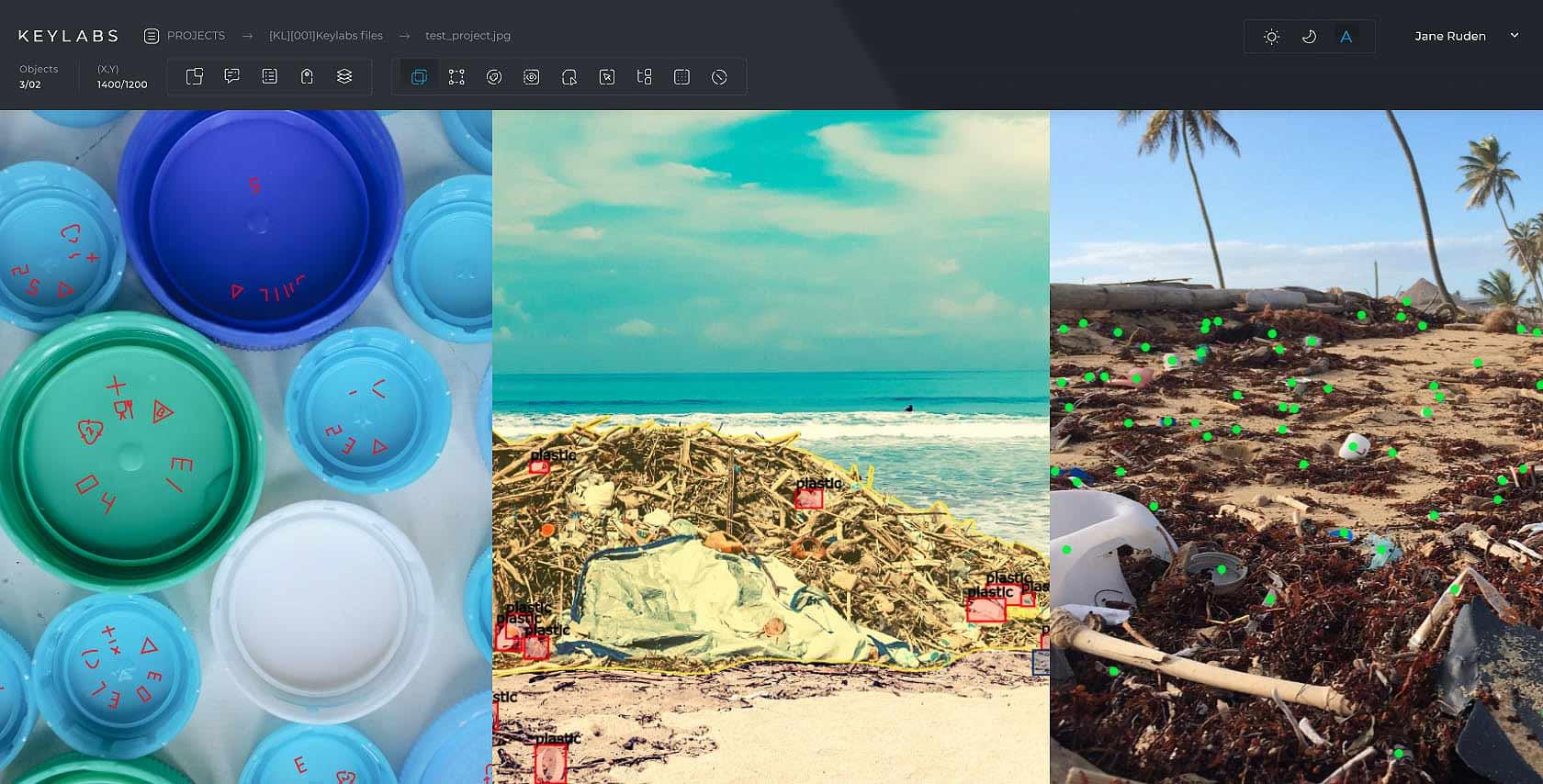
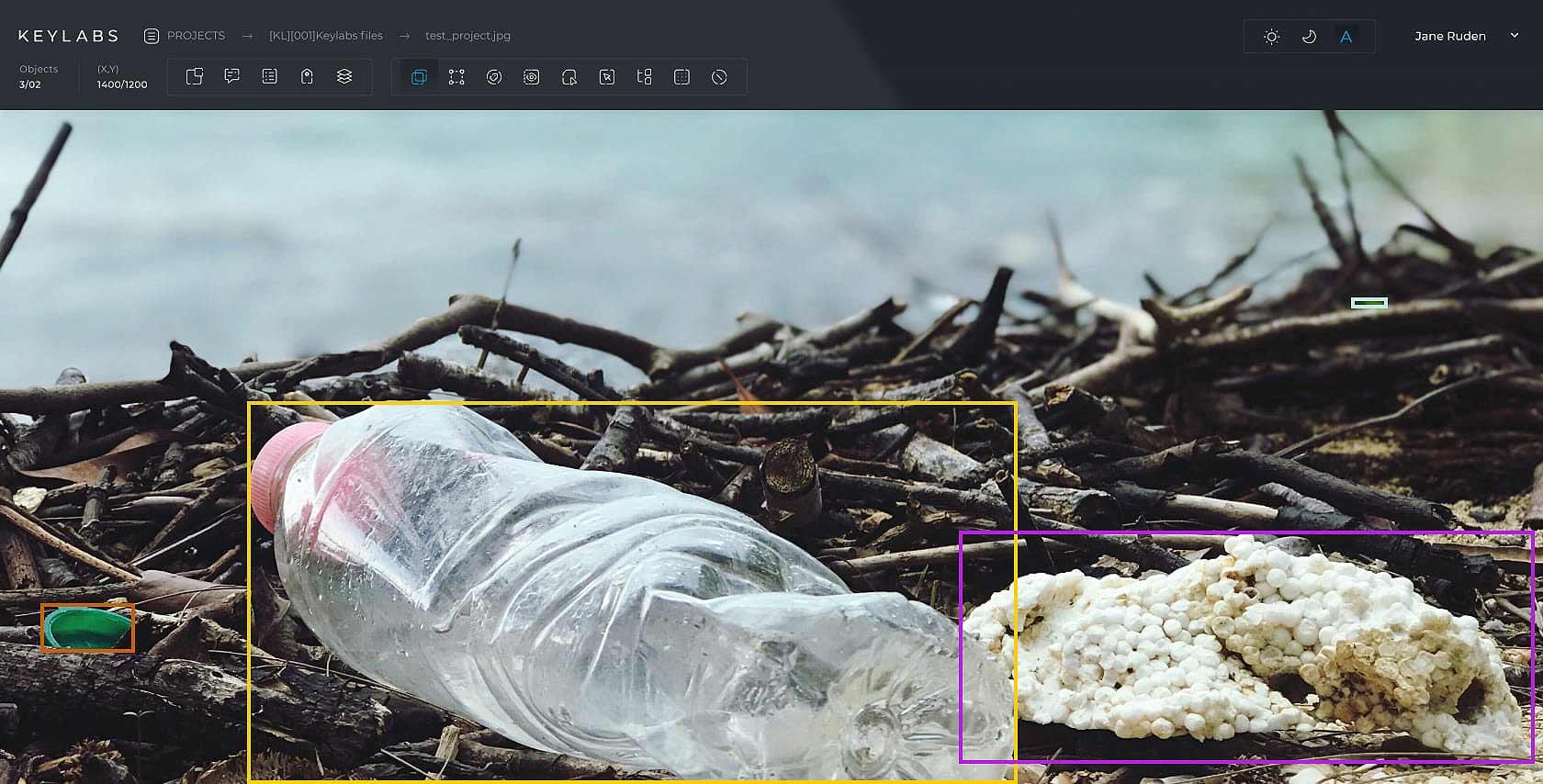
Accurate data annotation is crucial for successful machine learning in waste management. The process of annotating objects entering the waste stream is necessary to train computer vision systems to recognize and sort different types of waste. This technology has the potential to make recycling more efficient and cost-effective, as well as reduce plastic pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.

Data annotation tools
Some common applications for waste management systems:
Waste recognition and
classification
Annotated data is key to enhancing waste sorting through industrial robotics and AI algorithms. These technologies categorize materials more accurately, cutting down on manual labor and aiding in recycling and waste management. High-quality data annotation is essential, as it informs policies on environmental factors crucial for sustainable development. This approach not only makes recycling more efficient but also helps reduce plastic pollution and greenhouse gas emissions in industrial contexts.
Workflow and operational decisions
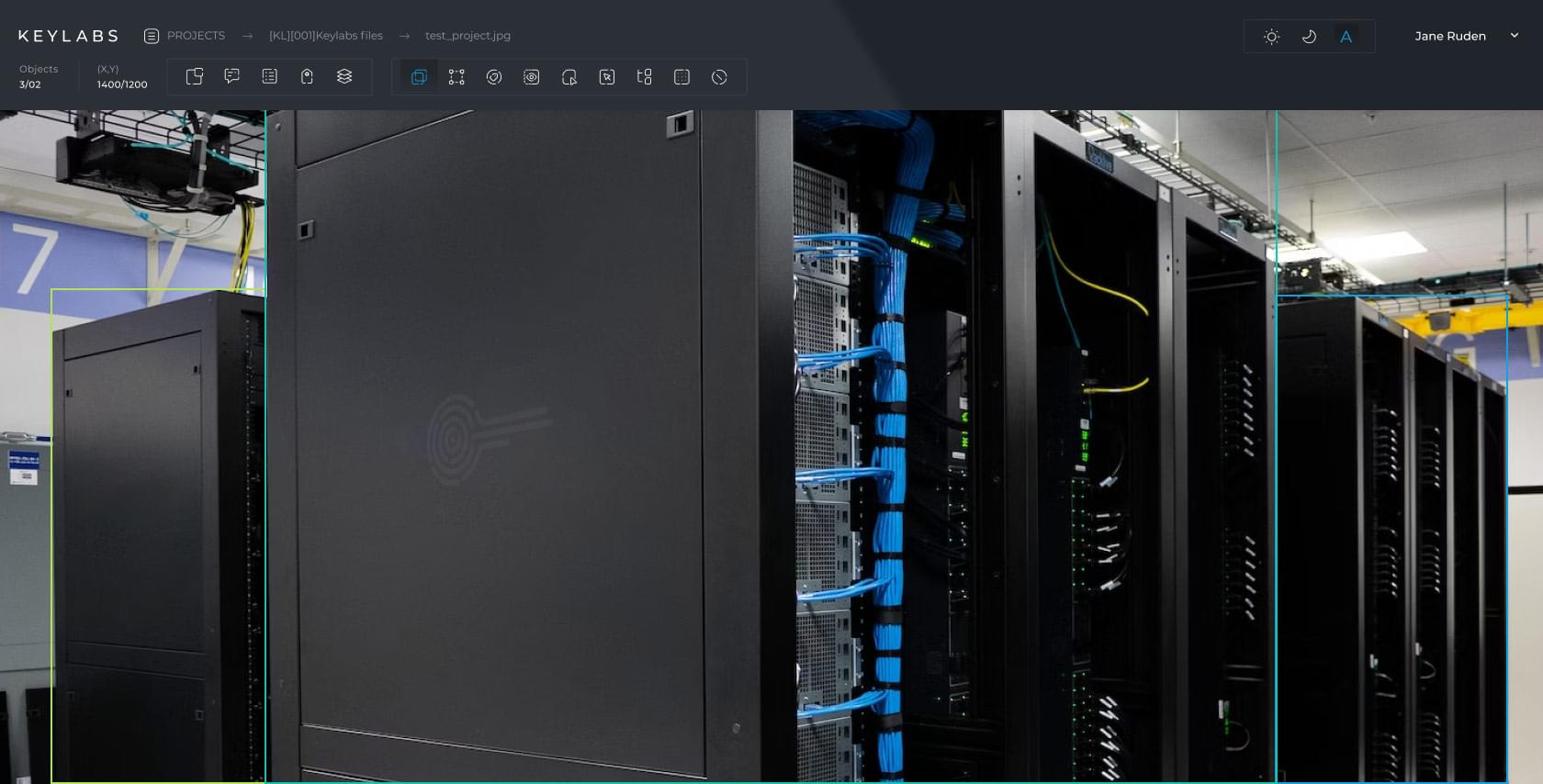
Keylabs' data annotation platform enhances waste management by allowing precise labeling of data using methods like bounding boxes and entity recognition. This aids in managing waste and related aspects, such as recycling and landfill space. Keylabs supports various data types and volumes, simplifying dataset management. Integrating machine learning for dataset labeling, it provides insights into waste origins, composition, and quantity, aiding both government and private sector in developing effective environmental strategies.
Real-time data analytics
Data annotation tools have become increasingly important in waste management due to the lack of benchmarks in waste detection, which slows down the optimization cycle and knowledge sharing. The semantic segmentation annotation method is required for waste product recognition in AI models, and Keylabs data annotation platform achieves precise semantic segmentation in waste management datasets. With the help of AI and robotics, numerous aspects of waste collection, transportation, sorting, and processing have been improved.
Key features
There are several key features that a robust data annotation tool for waste management should possess:
Versatility
The tool should be capable of handling different types of data, including 2D and 3D images, videos and point clouds generated by LiDAR sensors.
Precision
High-quality annotations are crucial for the accuracy of AI models in aerial management and disaster management. The tool should enable precise labeling of objects and features, minimizing the chances of misinterpretation.
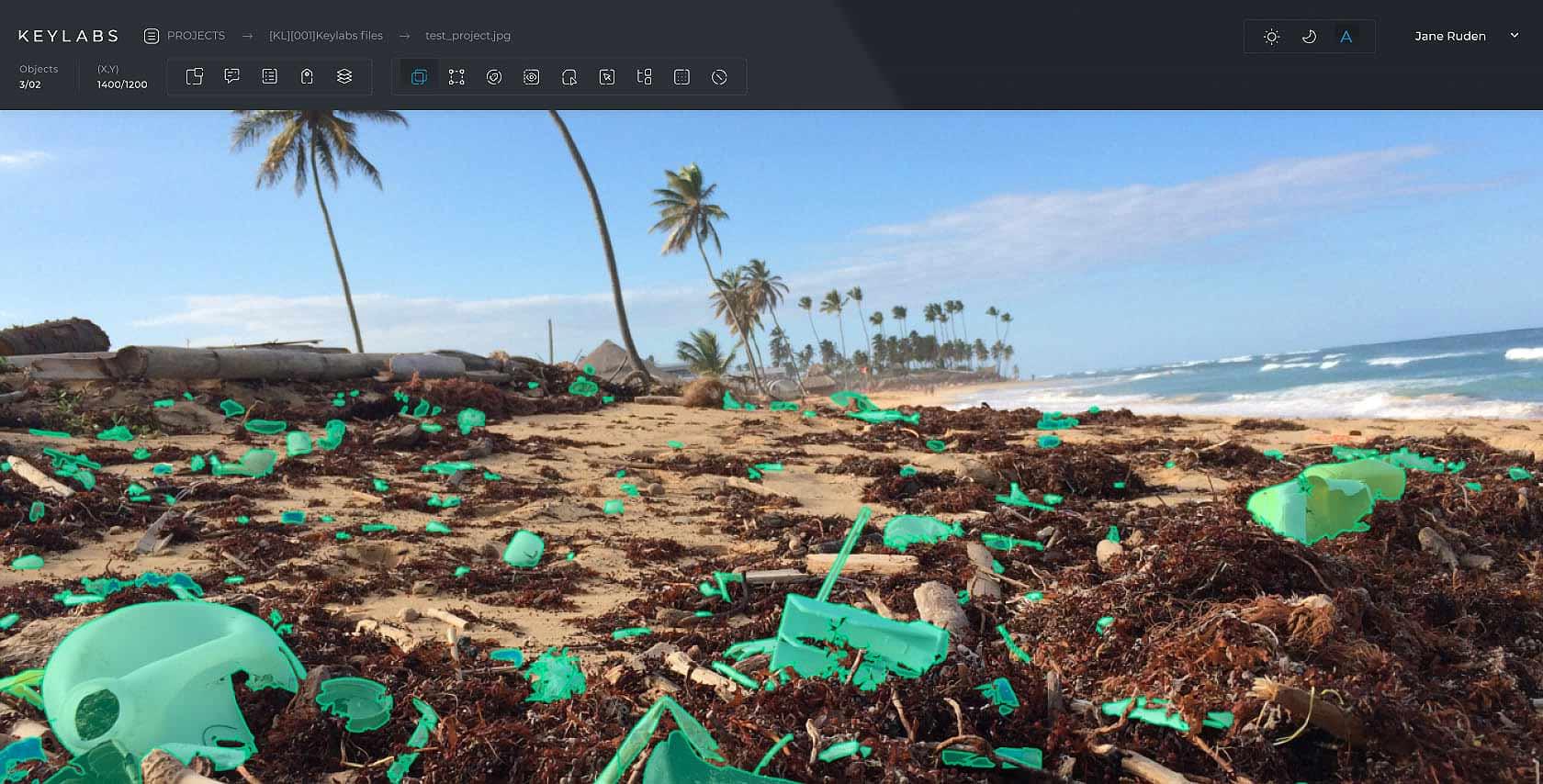
Scalability
A data annotation tool should be scalable to handle large datasets efficiently, streamlining the annotation process and reducing the time required for model training.

Automation
AI-powered data annotation tools can leverage machine learning algorithms to automate parts of the annotation process, speeding up the workflow and increasing overall efficiency.
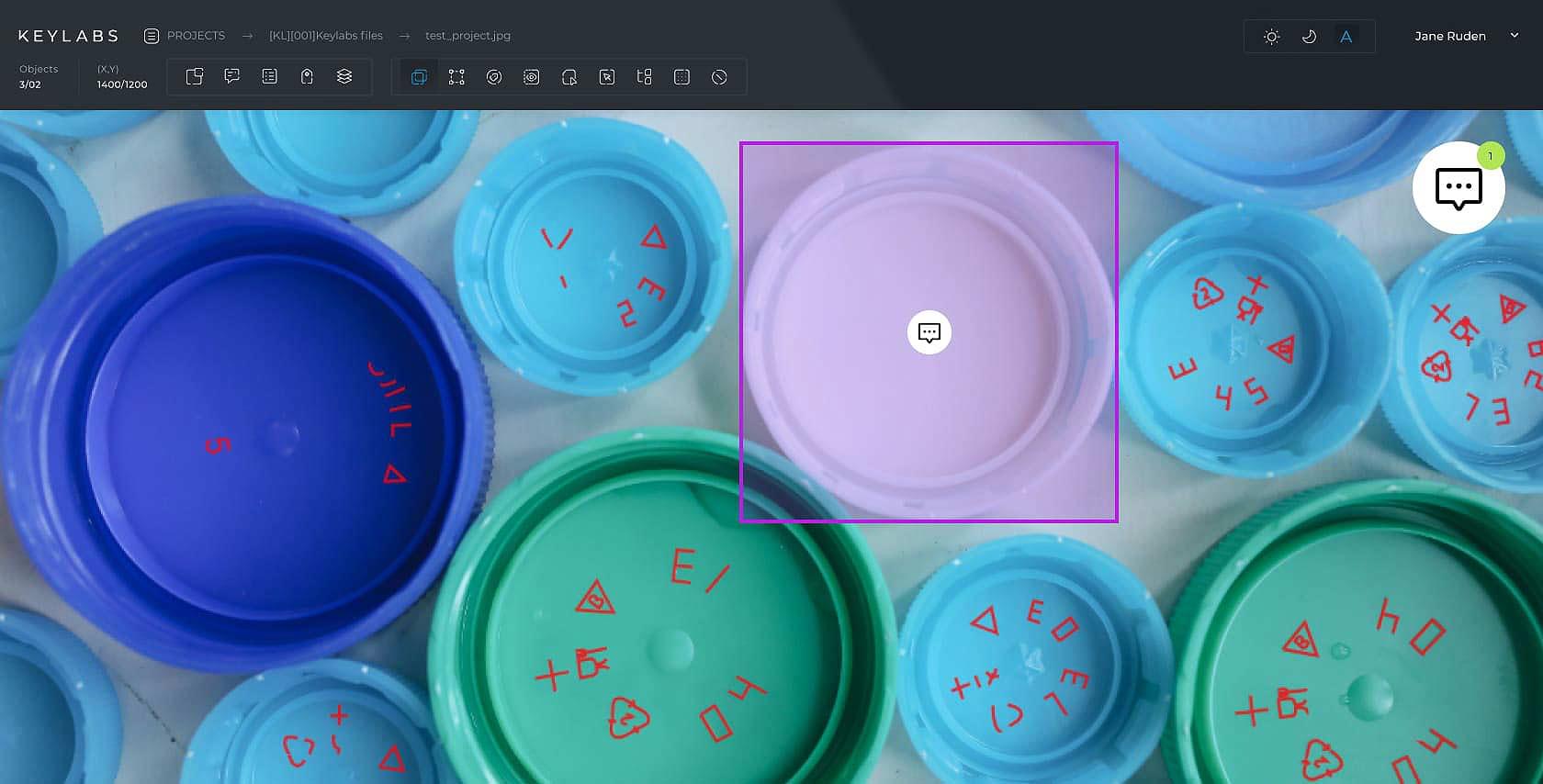
Collaboration
A good data annotation tool should facilitate collaboration among team members, enabling multiple annotators to work together on the same dataset. This ensures consistency in labeling and accelerates the annotation process.
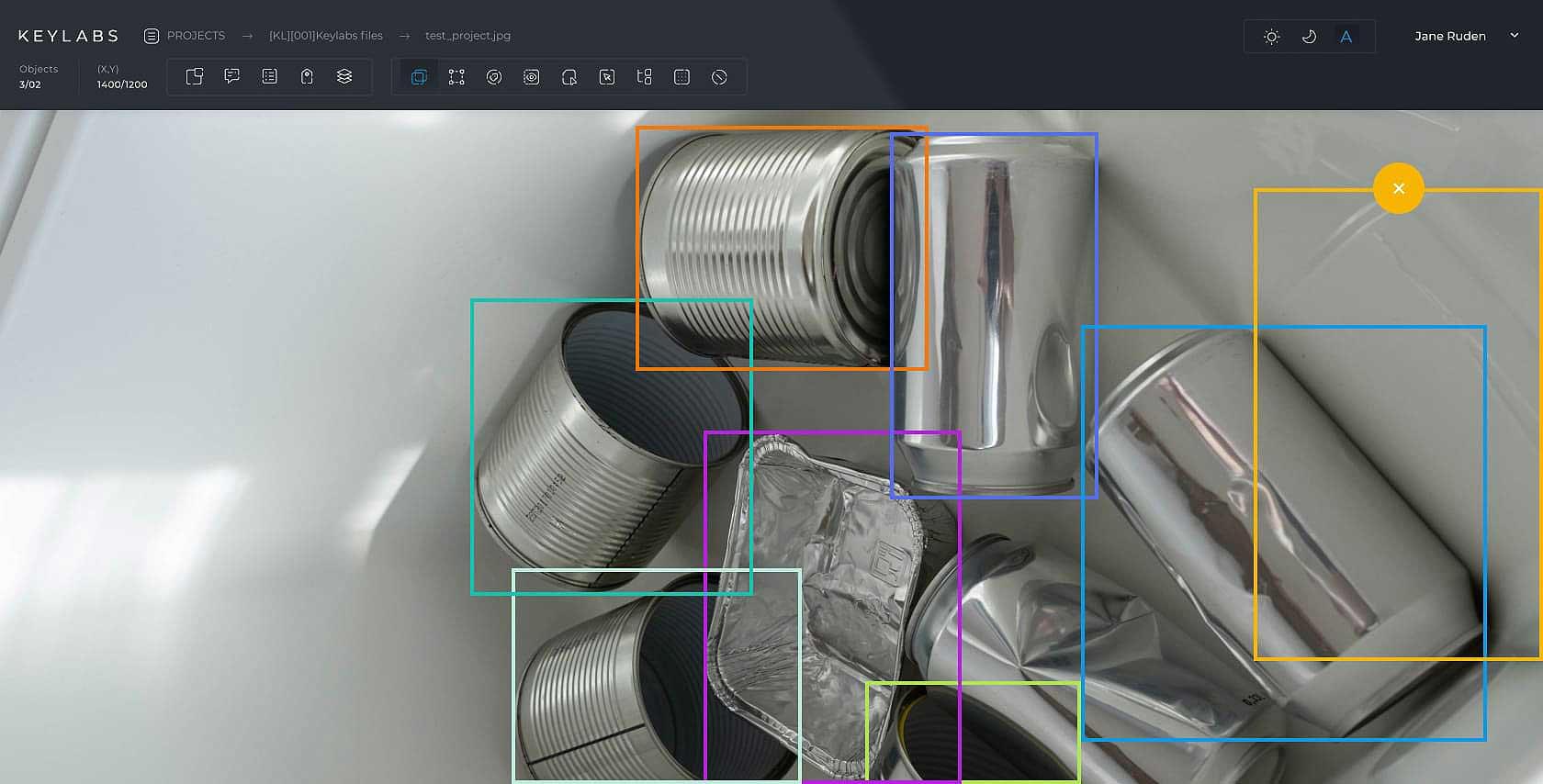
Quality control
To ensure the highest level of accuracy, the tool should have built-in quality control features that allow for easy review and verification of annotated data. This helps maintain data integrity and improves the overall performance of the AI models being trained.

Customization
The annotation requirements may change or become more complex. A flexible data annotation tool should allow for customization to meet the unique needs of each project and adapt to new challenges in the industry.
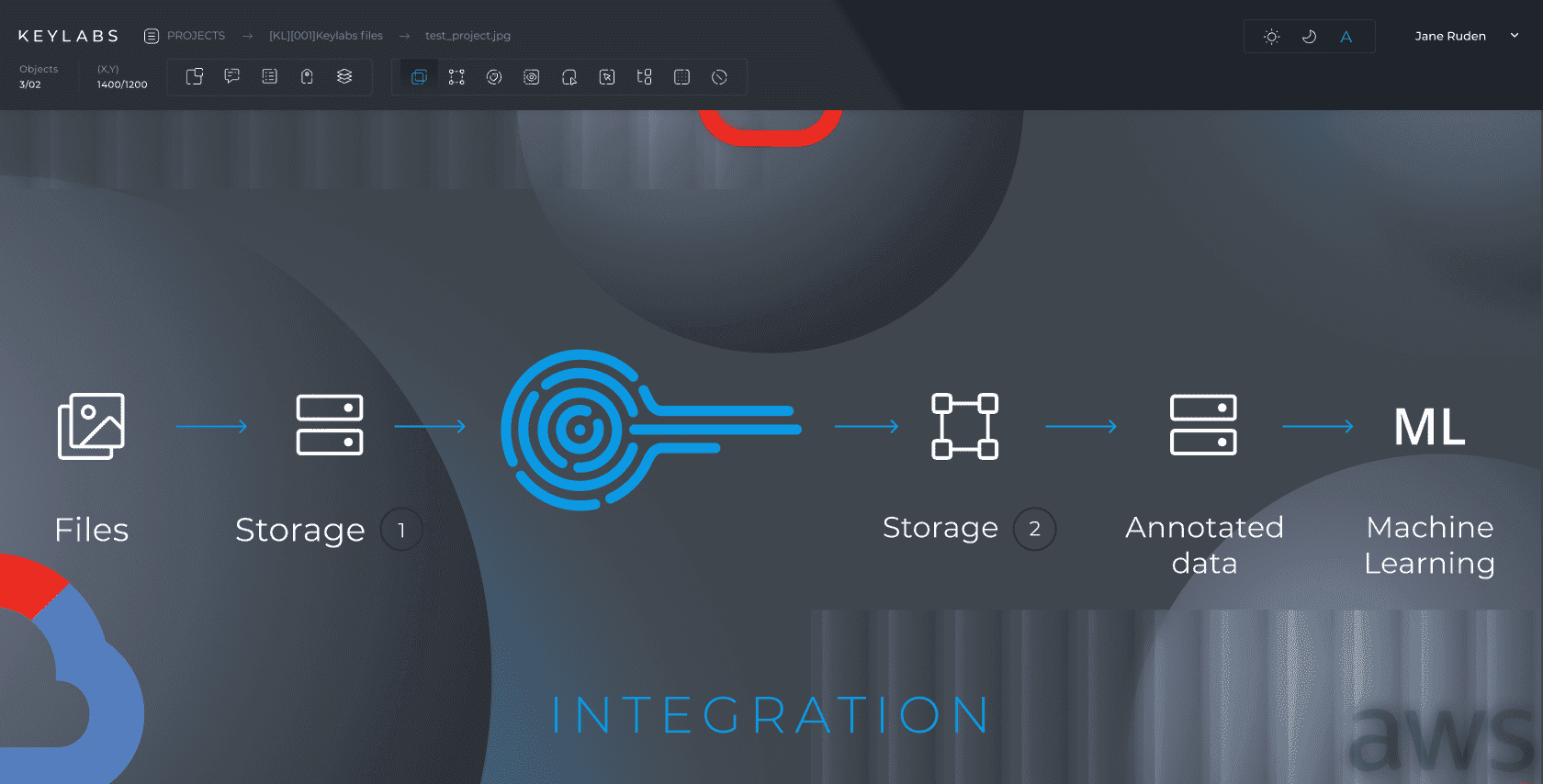
Integration
The data annotation tool should be able to integrate seamlessly with various machine learning frameworks and platforms, making it easier for developers to use the annotated data for model training and evaluation.

Data Security
A data annotation tool must prioritize data security and privacy, ensuring that the information is protected at all stages of the annotation process.
Versatility
Precision
Scalability
Automation
Collaboration
Quality Control
Customization
Integration
Data Security
Use cases
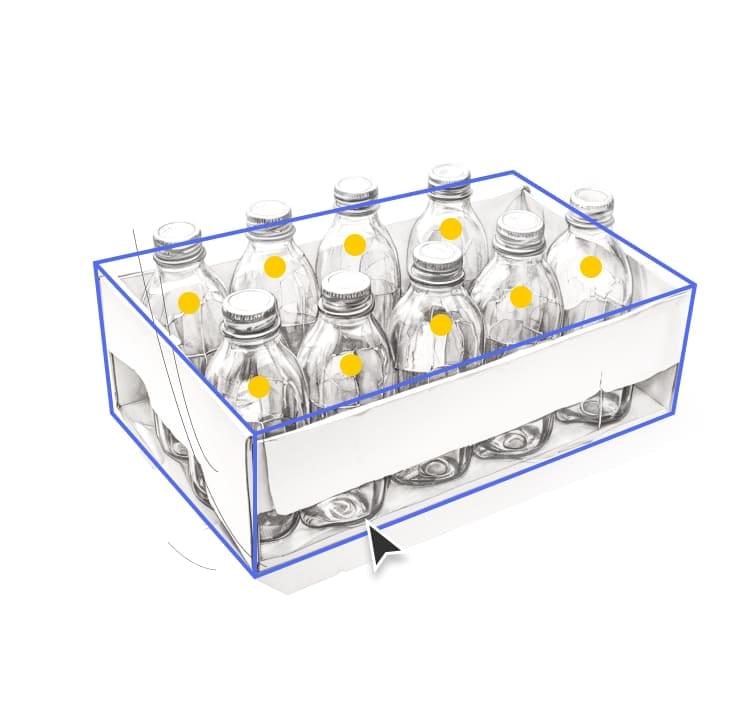

Recognition of recycling materials
In waste management, Keylabs excels at recognizing recycling materials, ensuring accurate identification and efficient sorting for sustainable practices.
Medical and biohazard waste
Keylabs adeptly handles the delicate task of identifying medical and biohazard waste, providing critical accuracy for safe and compliant waste handling.
Waste categorization
For waste categorization, Keylabs stands out with its precise dataset preparation, enabling effective sorting and management of diverse waste types.
Starter’s guide


Data security
Using the Keylabs annotation tools comes with a commitment to data safety. Keylabs employs a range of security measures to protect valuable and sensitive data. This includes comprehensive infrastructure security if you choose to access Keylabs through the cloud. Alternatively, Keylabs can be installed on premises, guaranteeing you total control over access. We will continue to emphasize data protections as a priority by utilizing a diverse array of security measures and industry best practices.
Top Features
Keylabs is created as a platform that incorporates state-of-the-art, performance oriented tools and processes.
ML assisted data annotation
ML assisted data annotation
Keylabs is a streamlined data labeling platform with AI-enhanced annotation.
Tailored for easy Integration with any client model and time & cost efficiency.
Keylabs’ advanced algorithms provide quick, accurate data prep for superior model training.
3D tool
3D tool
Keylabs is a super-fast tool, soaring through Lidar files at ultra speeds. It seamlessly handles all file formats, ensuring a consistent, efficient workflow regardless of file complexity.
High performance video annotation
High performance video annotation
With the Keylabs platform's technical and software capabilities, video annotation is highly accurate (precision of up to 99,9% depending on project needs) and fast. Thanks to the geolocation adaptation of servers, even big-sized videos are loaded and processed quickly.
Magic wand
Magic wand
Speeds up the annotation process by automatically detecting closed shapes of the same color or color gradient in a highly precise manner.
Object interpolation
Object interpolation
Object interpolation in the data annotation process is used to accelerate the annotation of objects across a sequence of frames in video annotation.
Annotators label the shape of an object in the first and the last keyframe of desired sequence and the object interpolation algorithm automatically generates the labels for the object in the intermediate frames.
It saves time and also ensures consistent labeling across frames.
A-Z order
A-Z order
Objects can be placed on different leveled layers, which allows operators to correctly detect and work with those objects and their boundaries.
Multilayer annotation
Multilayer annotation
Multilayer annotation is a complex yet valuable process in data annotation where different types of materials are layered onto a single item.
This allows the addition of multiple, diverse annotations to a single piece of data such as an image or video frame.
Each layer might provide a different dimension of information, enriching the dataset with multiple facets of detail.
This allows the addition of multiple, diverse annotations.
Object linking
Object linking
Object linking in the data annotation process is a valuable function that connects different instances of the same object across multiple frames or images.
For example, in video annotation, an object appearing in different frames is linked throughout the video, ensuring the continuity and consistency of the annotation.
Hierarchical atributes
Hierarchical atributes
The attribute is a type of tag that can be applied to a class or property to provide metadata about it.
Using attribute hierarchies, it is possible to define structures of metadata for each item in dataset.
It is achieved by using dependent attributes, which allows logical forming of metadata information for frame or object individually.
Workflow and task distribution
Workflow and task distribution
Workflow includes custom stages of one of 4 project stage types: annotation, verification, miscellanious and final.
Good workflow and task distribution ensure that the data annotation process is smooth, efficient and completed within the required timeframe.
Data management
Data management
Data management in the context of the data annotation process is about strategically handling and organizing the data throughout its lifecycle.
Effective data management helps to uphold data integrity and ensure that the final annotated data is accurate, consistent and ready for use in AI and machine learning projects.
Attributes interpolation
Attributes interpolation
Attributes metadata can also be interpolatable (changed) between the frames. For instance, In a self-driving car video annotation, this can label a car as a "sedan" going "30 mph" in the first frame & automatically estimate its type & speed in subsequent frames until the next key frame. This eliminates the need for manual annotation in each intervening frame, saving time & effort.
Annotation types
Keylabs gives developers access to a full suite of annotation techniques:
Bounding Box
A rectangular box defined by coordinates that encapsulates an object of interest within an image
Oriented bounding box
A rotated rectangle that tightly encloses an object, accommodating its orientation and shape more precisely than a standard bounding box
Polygon
A closed plane figure made up of several line segments that are joined together, used to define irregular shapes in an image
Points
The Point Annotation Tool places dots on images or videos, ideal for highlighting details like facial features, expressions and body postures
Lines & Multilines
A data annotation tool used to draw single or multiple interconnected lines on images, capturing linear features or paths
Skeleton
A thin version of a shape, representing its central structure and providing a simplified representation of its form, commonly used in understanding object morphology or structure
Instance Segmentation
The process of classifying and delineating each individual object instance in an image
Semantic Segmentation
The classification of each pixel in an image based on its semantic category, without distinguishing between individual object instances
Bitmask
A binary representation where each pixel value indicates whether it belongs to the object (1) or the background (0)
Cuboid
A 3D rectangular prism annotation, often used to represent objects in spatial dimensions
Mesh
A collection of vertices, edges and faces that define the shape of a 3D object in space, often used in 3D modeling and computer graphics
3D Point Cloud
A collection of data points in a three-dimensional coordinate system, representing the external surface of an object
Custom
A tailored data annotation tool designed to cater to specific annotation needs not covered by standard tools